3Com 2916-SFP User Guide - Page 110
Configuring ARP Settings, Configuration Method, IP Address, Subnet Mask, Default Gateway, Apply
 |
UPC - 662705518893
View all 3Com 2916-SFP manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 110 highlights
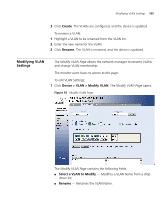
110 CHAPTER 9: CONFIGURING IP AND MAC ADDRESS INFORMATION The IP Setup Page contains the following fields: ■ Configuration Method - Indicates if the IP address has been configured statically or added dynamically. The possible field values are: ■ Static - Indicates that the IP Interface is configured by the user. ■ DHCP - Indicates that the IP Interface is dynamically created. ■ IP Address - Displays the currently configured IP address. ■ Subnet Mask - Displays the currently configured subnet mask. ■ Default Gateway - Displays the currently configured default gateway. 2 Select Manual or DHCP mode. 3 If Manual has been selected, configure the IP Address, Subnet Mask and Default Gateway. 4 Click Apply. The IP configuration is enabled, and the device is updated. Configuring ARP Settings The Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) converts IP addresses into physical addresses, and maps the IP address to a MAC address. ARP allows a host to communicate with other hosts when only the IP address of its neighbors is known. This section includes the following sections: ■ Viewing ARP Settings ■ Defining ARP Settings ■ Removing ARP Entries