Casio FX300MS User Guide - Page 23
Statistical, Calculations
 |
View all Casio FX300MS manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 23 highlights
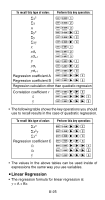
• Example 2: To convert rectangular coordinates (1, 3) to polar coordinates (r,) (Rad) r ҃ 2 f1P L3T= θ ҃ 1.047197551 0 o • Press 0 n to display the value of r, or 0 o to display the value of . k Engineering Notation Calculations • Example 1: To convert 56,088 meters to kilometers → 56.088 ҂103 (km) 56088 = J • Example 2: To convert 0.08125 grams to milligrams → 81.25 ҂10 -3 (mg) 0.08125 = J Statistical SD Calculations REG Standard Deviation SD Use the F key to enter the SD Mode when you want to perform statistical calculations using standard deviation. SD F 2 • In the SD Mode and REG Mode, the | key operates as the S key. • Always start data input with A B 1(Scl) = to clear statistical memory. • Input data using the key sequence shown below. S • Input data is used to calculate values for n, Σx, Σx2, o, σn and σn-1, which you can recall using the key opera- tions noted nearby. E-21