Casio FX300MS User Guide - Page 29
Logarithmic, Exponential, Power, and Inverse, Regression, Quadratic Regression
 |
View all Casio FX300MS manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 29 highlights
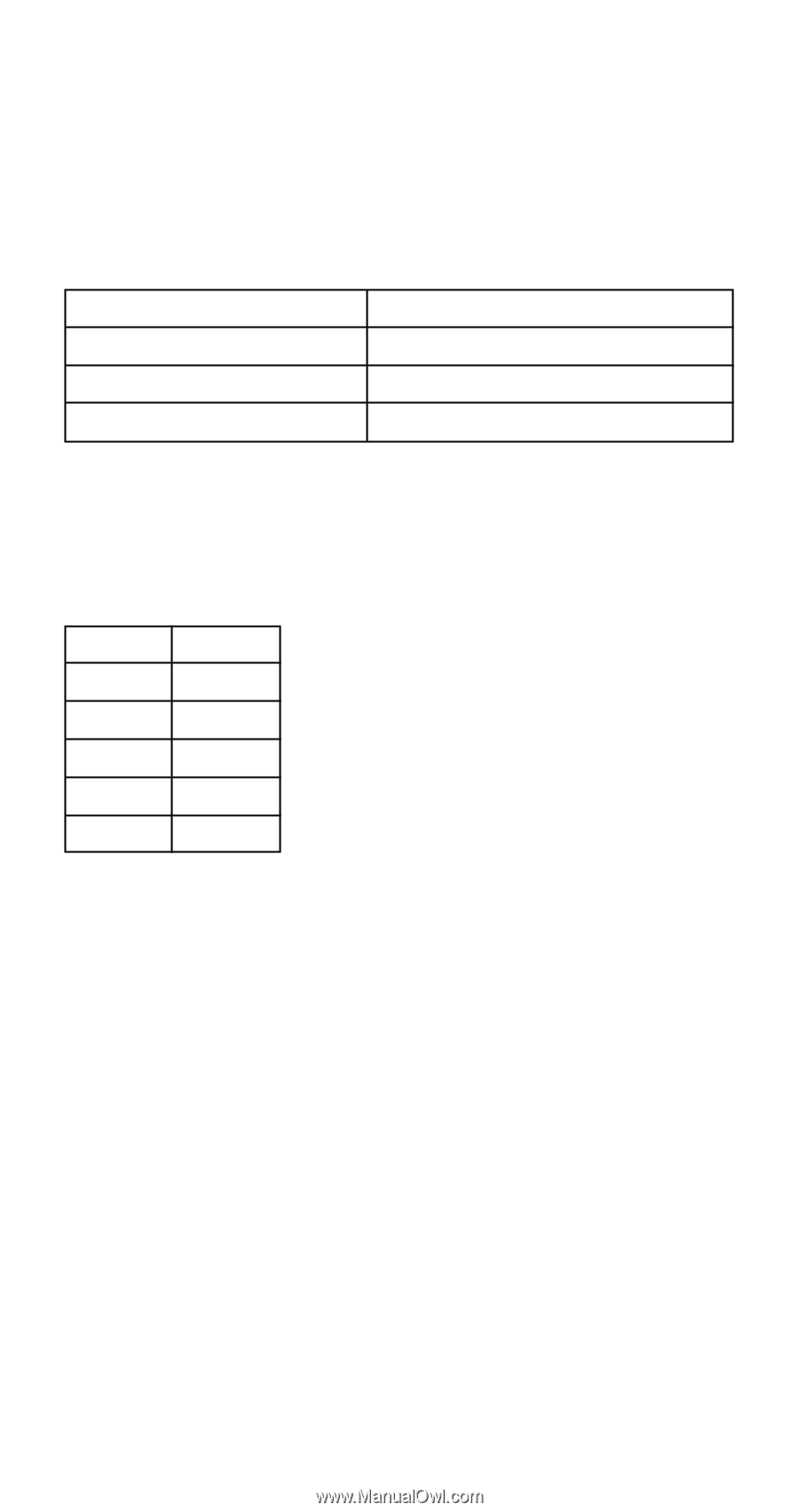
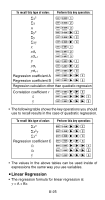
u Logarithmic, Exponential, Power, and Inverse Regression • Use the same key operations as linear regression to recall results for these types of regression. • The following shows the regression formulas for each type of regression. Logarithmic Regression y ҃ A ѿ B ؒ In x Exponential Regression y ҃ A ؒ eB·x (In y ҃ In A + Bx) Power Regression y ҃ A ؒ xB (In y ҃ In A + BIn x) Inverse Regression y ҃ A ѿ B ؒ 1/x u Quadratic Regression • The regression formula for quadratic regression is: y = A + Bx + Cx2. • Example: xi yi 29 1.6 50 23.5 74 38.0 103 46.4 118 48.0 Perform quadratic regression to de- termine the regression formula terms for the data nearby. Next, use the regression formula to estimate the values for n (estimated value of y) for xi = 16 and m (estimated value of x) for yi = 20. In the REG Mode: r 3(Quad) A B 1 (Scl) = (Stat clear) 29 P 1.6 S 50 P 23.5 S 74 P 38.0 S 103 P 46.4 S 118 P 48.0 S Regression Coefficient A = -35.59856934 A X r r 1 = Regression Coefficient B = 1.495939413 A X r r 2 = Regression Coefficient C = - 6.71629667 i10 -3 A X r r 3 = n when xi is 16 = -13.38291067 16 A X r r r 3 = m1 when yi is 20 = 47.14556728 20 A X r r r 1 = m2 when yi is 20 = 175.5872105 20 A X r r r 2 = E-27