Cisco 3825 User Guide - Page 57
Perfect Forward Secrecy PFS, Inbound SPI/Outbound SPI - vpn
 |
UPC - 746320981505
View all Cisco 3825 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 57 highlights
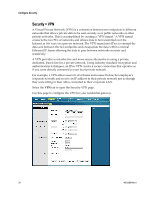
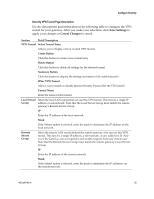
Configure Security Section Field Description Key Select one of the following options for the key exchange method: Management (continued) ƒ Auto (IKE) - Encryption: The Encryption method determines the length of the key used to encrypt/decrypt ESP packets. Notice that both sides must use the same method. - Authentication: The Authentication method authenticates the Encapsulating Security Payload (ESP) packets. Select MD5 or SHA. Notice that both sides (VPN endpoints) must use the same method. ƒ MD5: A one-way hashing algorithm that produces a 128-bit digest ƒ SHA: A one-way hashing algorithm that produces a 160-bit digest - Perfect Forward Secrecy (PFS): If PFS is enabled, IKE Phase 2 negotiation will generate new key material for IP traffic encryption and authentication. Note that both sides must have PFS enabled. - Pre-Shared Key: IKE uses the Pre-Shared Key to authenticate the remote IKE peer. Both character and hexadecimal values are acceptable in this field, e.g., "My_@123" or "0x4d795f40313233". Note that both sides must use the same Pre-Shared Key. - Key Lifetime: This field specifies the lifetime of the IKE generated key. If the time expires, a new key will be renegotiated automatically. The Key Lifetime may range from 300 to 100,000,000 seconds. The default lifetime is 3600 seconds. ƒ Manual - Encryption: The Encryption method determines the length of the key used to encrypt/decrypt ESP packets. Notice that both sides must use the same method. - Encryption Key: This field specifies a key used to encrypt and decrypt IP traffic. Both character and hexadecimal values are acceptable in this field. Note that both sides must use the same Encryption Key. - Authentication: The Authentication method authenticates the Encapsulating Security Payload (ESP) packets. Select MD5 or SHA. Notice that both sides (VPN endpoints) must use the same method. ƒ MD5: A one-way hashing algorithm that produces a 128-bit digest ƒ SHA: A one-way hashing algorithm that produces a 160-bit digest - Authentication Key: This field specifies a key used to authenticate IP traffic. Both character and hexadecimal values are acceptable in this field. Note that both sides must use the same Authentication Key. - Inbound SPI/Outbound SPI: The Security Parameter Index (SPI) is carried in the ESP header. This enables the receiver to select the SA, under which a packet should be processed. The SPI is a 32-bit value. Both decimal and hexadecimal values are acceptable. e.g., "987654321" or "0x3ade68b1". Each tunnel must have a unique Inbound SPI and Outbound SPI. No two tunnels share the same SPI. Note that the Inbound SPI must match the remote gateway's Outbound SPI, and vice versa. 4021196 Rev A 57