Cisco 6941 Administration Guide - Page 154
Troubleshooting Tips, Using Voice-Quality Metrics
 |
UPC - 882658277801
View all Cisco 6941 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 154 highlights
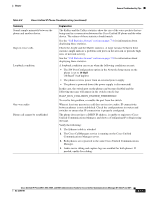
Monitoring the Voice Quality of Calls Chapter Troubleshooting Tips When you observe significant and persistent changes to metrics, use Table 9-4 for general troubleshooting information. Table 9-4 Changes to Voice Quality Metrics Metric Change Condition Conceal Ratio and Conceal Network impairment from packet loss or high jitter. Seconds increase significantly Conceal Ratio is near or at zero, • Noise or distortion in the audio channel such as echo or but the voice quality is poor. audio levels. • Tandem calls that undergo multiple encode/decode such as calls to a cellular network or calling card network. • Acoustic problems coming from a speakerphone, handsfree cellular phone or wireless headset. Check packet transmit (TxCnt) and packet receive (RxCnt) counters to verify that voice packets are flowing. MOS LQK scores decrease significantly Network impairment from packet loss or high jitter levels: • Average MOS LQK decreases may indicate widespread and uniform impairment. • Individual MOS LQK decreases may indicate bursty impairment. Cross-check the conceal ratio and conceal seconds for evidence of packet loss and jitter. MOS LQK scores increase significantly • Check to see if the phone is using a different codec than expected (RxType and TxType). • Check to see if the MOS LQK version changed after a firmware upgrade. Note Voice quality metrics do not account for noise or distortion, only frame loss. Using Voice-Quality Metrics When using the metrics for monitoring voice quality, note the typical scores under normal conditions of zero packet loss and use the metrics as a baseline for comparison. It is also important to distinguish significant changes from random changes in metrics. Significant changes are scores that change about 0.2 MOS or more and persist in calls that last longer than 30 seconds. Conceal ratio changes indicate a frame loss greater than 3 percent. The MOS LQK scores can vary based on the codec that the Cisco Unified IP Phone uses. The following codecs provide these corresponding maximum MOS LQK scores under normal conditions with zero frame loss for Cisco Unified Phones 6921, 6941, 6945, and 6961: • G.711: 4.5 MOS LQK • G.722: 4.5 MOS LQK 9-14 Cisco Unified IP Phone 6921, 6941, 6945, and 6961 Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager 8.5 (SCCP and SIP) OL-23769-01