Cisco 6941 Administration Guide - Page 22
Networking Protocol, Purpose, Usage Notes, Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol, Cisco TFTP - ip phone manual
 |
UPC - 882658277801
View all Cisco 6941 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 22 highlights
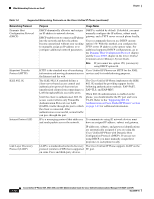
What Networking Protocols are Used? Chapter Table 1-4 Supported Networking Protocols on the Cisco Unified IP Phone (continued) Networking Protocol Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) IEEE 802.1X Internet Protocol (IP) Link Layer Discovery Protocol (LLDP) Purpose Usage Notes DHCP dynamically allocates and assigns an IP address to network devices. DHCP enables you to connect an IP phone into the network and have the phone become operational without your needing to manually assign an IP address or to configure additional network parameters. DHCP is enabled by default. If disabled, you must manually configure the IP address, subnet mask, gateway, and a TFTP server on each phone locally. Cisco recommends that you use DHCP custom option 150. With this method, you configure the TFTP server IP address as the option value. For additional supported DHCP configurations, go to the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol chapter and the Cisco TFTP chapter in the Cisco Unified Communications Manager System Guide. Note If you cannot use option 150, you may try using DHCP option 66. HTTP is the standard way of transferring Cisco Unified IP Phones use HTTP for the XML information and moving documents across services and for troubleshooting purposes. the Internet and the web. The IEEE 802.1X standard defines a client-server-based access control and authentication protocol that restricts unauthorized clients from connecting to a LAN through publicly accessible ports. Until the client is authenticated, 802.1X access control allows only Extensible Authentication Protocol over LAN (EAPOL) traffic through the port to which the client is connected. After authentication is successful, normal traffic can pass through the port. The Cisco Unified IP Phone implements the IEEE 802.1X standard by providing support for the following authentication methods: EAP-FAST, EAP-TLS, and EAP-MD5. When 802.1X authentication is enabled on the phone, you should disable the PC port and voice VLAN. Refer to the "Supporting 802.1X Authentication on Cisco Unified IP Phones" section on page 1-21 for additional information. IP is a messaging protocol that addresses To communicate using IP, network devices must and sends packets across the network. have an assigned IP address, subnet, and gateway. IP addresses, subnets, and gateways identifications are automatically assigned if you are using the Cisco Unified IP Phone with Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP). If you are not using DHCP, you must manually assign these properties to each phone locally. LLDP is a standardized network discovery The Cisco Unified IP Phone supports LLDP on the protocol (similar to CDP) that is supported PC port. on some Cisco and third-party devices. 1-10 Cisco Unified IP Phone 6921, 6941, 6945, and 6961 Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager 8.5 (SCCP and SIP) OL-23769-01