Cisco WS-C3560-8PC-S Installation Guide - Page 53
Small- to Medium-Sized Network Configuration
 |
UPC - 882658120404
View all Cisco WS-C3560-8PC-S manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 53 highlights
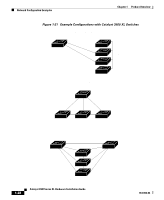
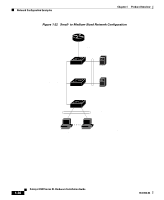
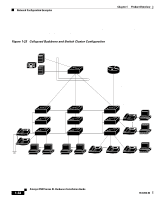
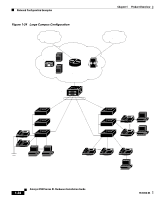
Chapter 1 Product Overview Network Configuration Examples Small- to Medium-Sized Network Configuration Figure 1-22 illustrates a configuration for a network that has up to 250 users. Users in this network require e-mail, file-sharing, database, and Internet access. You optimize network performance by placing workstations on the same logical segment as the servers they access most often. This divides the network into smaller segments (or workgroups) and reduces the amount of traffic that travels over a network backbone, thereby increasing the bandwidth available to each user and improving server response time. A network backbone is a high-bandwidth connection (such as Fast Ethernet or Gigabit Ethernet) that interconnects segments and network resources. It is required if numerous segments require access to the servers. The Catalyst 3500 XL switches in this network are connected through a GigaStack GBIC on each switch to form a 1-Gbps network backbone. This GigaStack also can be configured as a switch cluster, with primary and secondary command switches for redundant cluster management. Workstations are connected directly to the 10/100 switch ports for their own 10- or 100-Mbps access to network resources (such as web and mail servers). When a workstation is configured for full-duplex operation, it receives up to 200 Mbps of dedicated bandwidth from the switch. Servers are connected to the gigabit GBIC module ports on the switches, allowing 1-Gbps throughput to users when needed. When the switch and server ports are configured for full-duplex operation, the links provide 2 Gbps of bandwidth. For networks that do not require gigabit performance from a server, connect the server to a Fast Ethernet or Fast EtherChannel switch port. Connecting a router to a Fast Ethernet switch port provides multiple, simultaneous access to the Internet through one line. 78-6456-04 Catalyst 3500 Series XL Hardware Installation Guide 1-29