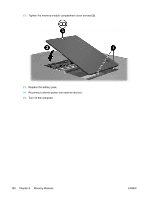
Compaq Presario V5000 User Guide - Page 119
wireless devices (select models only)
 |
View all Compaq Presario V5000 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 119 highlights
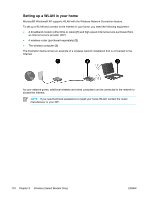
802.11 wireless devices (select models only) A computer with an 802.11 wireless device can access a wireless local area network (commonly referred to as wireless network, wireless LAN, or WLAN), which is composed of other computers and accessories linked by a wireless router or a wireless access point: ● A home or small office WLAN typically uses a wireless router, which enables several wireless and wired computers to share an Internet connection, a printer, and files without additional pieces of hardware or software. NOTE The terms wireless access point and wireless router are often used interchangeably. ● A large-scale WLAN, such as a corporate or public WLAN, typically uses wireless access points that can handle a large number of computers and accessories and can separate critical network functions. 802.11 wireless devices include: ● 802.11b ● 802.11b/g ● 802.11a/b/g Computers with 802.11 wireless devices may support 1 or more of 3 industry standards: ● 802.11b supports data rates of up to 11 Mbps and operates at a frequency of 2.4 GHz. ● 802.11g supports data rates of up to 54 Mbps and operates at a frequency of 2.4 GHz. An 802.11g WLAN device is backward compatible with 802.11b devices, so they can operate on the same network. ● 802.11a supports data rates of up to 54 Mbps and operates at a frequency of 5 GHz. 802.11a is not compatible with 802.11b and 802.11g. For information on identifying the wireless device in the computer, refer to "Identifying an 802.11 wireless device." ENWW 802.11 wireless devices (select models only) 109