D-Link DFL-260 Product Manual - Page 172
A Simple OSPF Scenario, OSPF is not available on all D-Link NetDefend models - d link dfl 260 e
 |
UPC - 790069296802
View all D-Link DFL-260 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 172 highlights
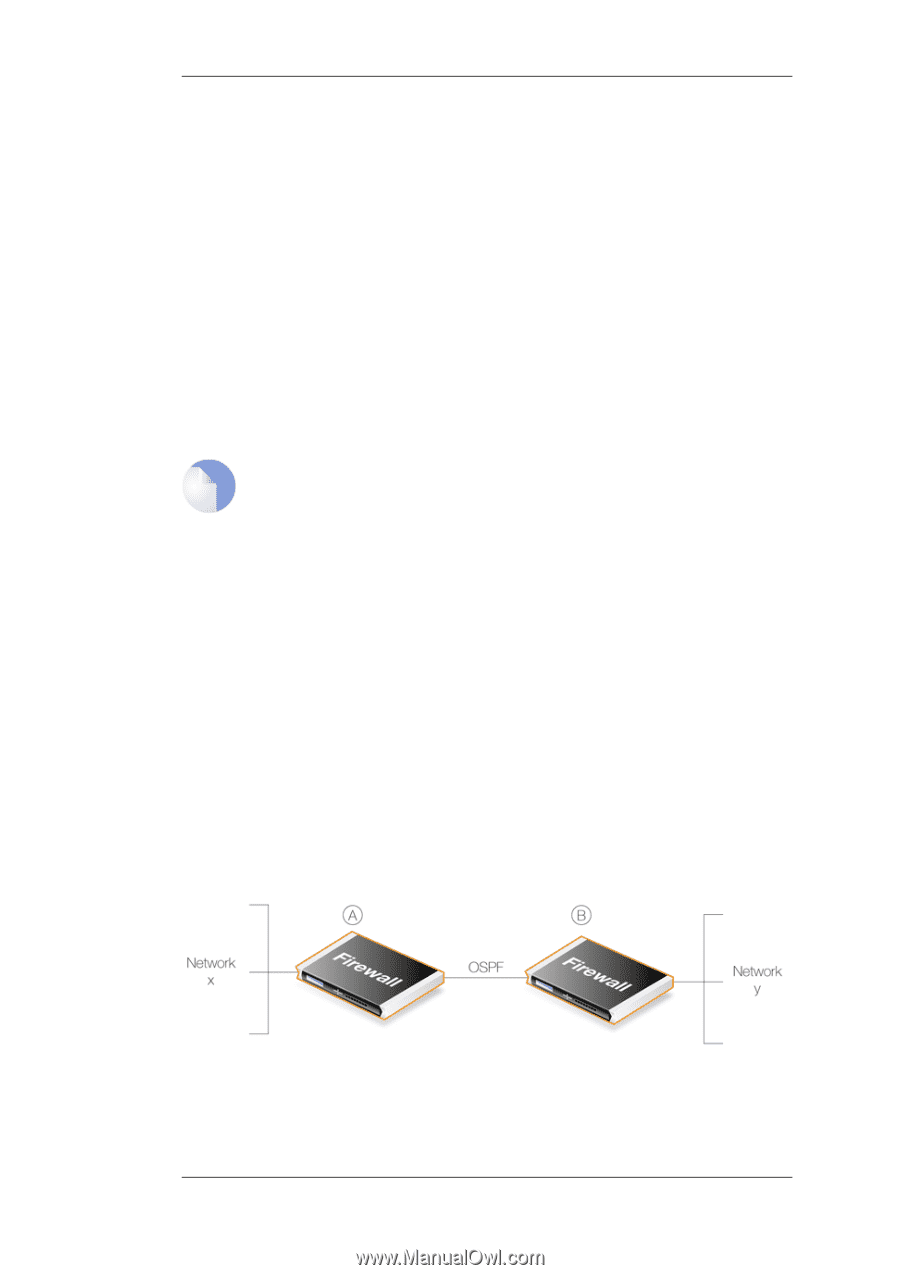
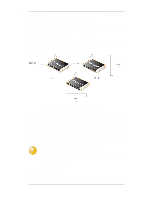
4.5.1. Dynamic Routing Chapter 4. Routing Each router broadcasts its attached links and link costs to all other routers in the network. When a router receives these broadcasts it runs the LS algorithm and calculates its own set of least-cost paths. Any change of the link state will be sent everywhere in the network, so that all routers keep the same routing table information and have a consistent view of the network. Advantages of Link State Algorithms Due to the fact that the global link state information is maintained everywhere in a network, LS algorithms, like that used in OSPF, offer a high degree of configuration control and scalability. Changes result in broadcasts of just the updated information to other routers which means faster convergence and less possibility of routing loops. OSPF can also function within a hierarchy, whereas RIP has no knowledge of sub-network addressing. The OSPF Solution Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) is a widely used protocol based on an LS algorithm. Dynamic routing is implemented in NetDefendOS using OSPF. OSPF is not available on all D-Link NetDefend models The OSPF feature is only available on the D-Link NetDefend DFL-800, 860, 1600, 1660 2500, 2560 and 2560G. OSPF is not available on the DFL-210 and 260. An OSPF enabled router first identifies the routers and sub-networks that are directly connected to it and then broadcasts the information to all the other routers. Each router uses the information it receives to add the OSPF learned routes to its routing table. With this larger picture, each OSPF router can identify the networks and routers that lead to a given destination IP and therefore the best route. Routers using OSPF then only broadcast updates to inform others of any route changes instead of broadcasting the entire routing table. OSPF depends on various metrics for path determination, including hops, bandwidth, load and delay. OSPF can also provide a high level of control over the routing process since its parameters can be finely tuned. A Simple OSPF Scenario The simple network topology illustrated below provides an excellent example of what OSPF can achieve. Here we have two NetDefend Firewalls A and B connected together and configured to be in the same OSPF area (the concept of area will be explained later). Figure 4.8. A Simple OSPF Scenario OSPF allows firewall A to know that to reach network Y, traffic needs to be sent to firewall B. Instead of having to manually insert this routing information into the routing tables of A, OSPF 172