D-Link DI-634M Product Manual - Page 82
What is DMZ?, How do I configure the DMZ Host? - product manual
 |
UPC - 790069282676
View all D-Link DI-634M manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 82 highlights
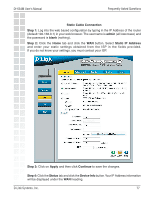
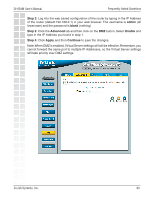
DI-634M User's Manual 6) What is DMZ? Frequently Asked Questions Demilitarized Zone: In computer networks, a DMZ (demilitarized zone) is a computer host or small network inserted as a neutral zone between a company´s private network and the outside public network. It prevents outside users from getting direct access to a server that has company data. The term comes from the geographic buffer zone that was set up between North Korea and South Korea following the UN police action in the early 1950s. A DMZ is an optional and more secure approach to a firewall and effectively acts as a proxy server as well. In a typical DMZ configuration for a small company, a separate computer (or host in network terms) receives requests from users within the private network for access to Web sites or other companies accessible on the public network. The DMZ host then initiates sessions for these requests on the public network. However, the DMZ host is not able to initiate a session back into the private network. It can only forward packets that have already been requested. Users of the public network outside the company can access only the DMZ host. The DMZ may typically also have the company´s Web pages so these could be served to the outside world. However, the DMZ provides access to no other company data. In the event that an outside user penetrated the DMZ hosts security, the Web pages might be corrupted but no other company information would be exposed. D-Link, a leading maker of routers, is one company that sells products designed for setting up a DMZ 7) How do I configure the DMZ Host? The DMZ feature allows you to forward all incoming ports to one computer on the local network. The DMZ, or Demilitarized Zone, will allow the specified computer to be exposed to the Internet. DMZ is useful when a certain application or game does not work through the firewall. The computer that is configured for DMZ will be completely vulnerable on the Internet, so it is suggested that you try opening ports from the Virtual Server or Firewall settings before using DMZ. Step 1: Find the IP address of the computer you want to use as the DMZ host. To find out how to locate the IP Address of the computer in Windows XP/2000/Me/9x or Macintosh operating systems please refer to Step 4 of the first question in this section (Frequently Asked Questions). D-Link Systems, Inc. 82