D-Link DNS-321 User Manual - Page 48
What is RAID?, RAID 0 - speed
 |
UPC - 790069314162
View all D-Link DNS-321 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 48 highlights
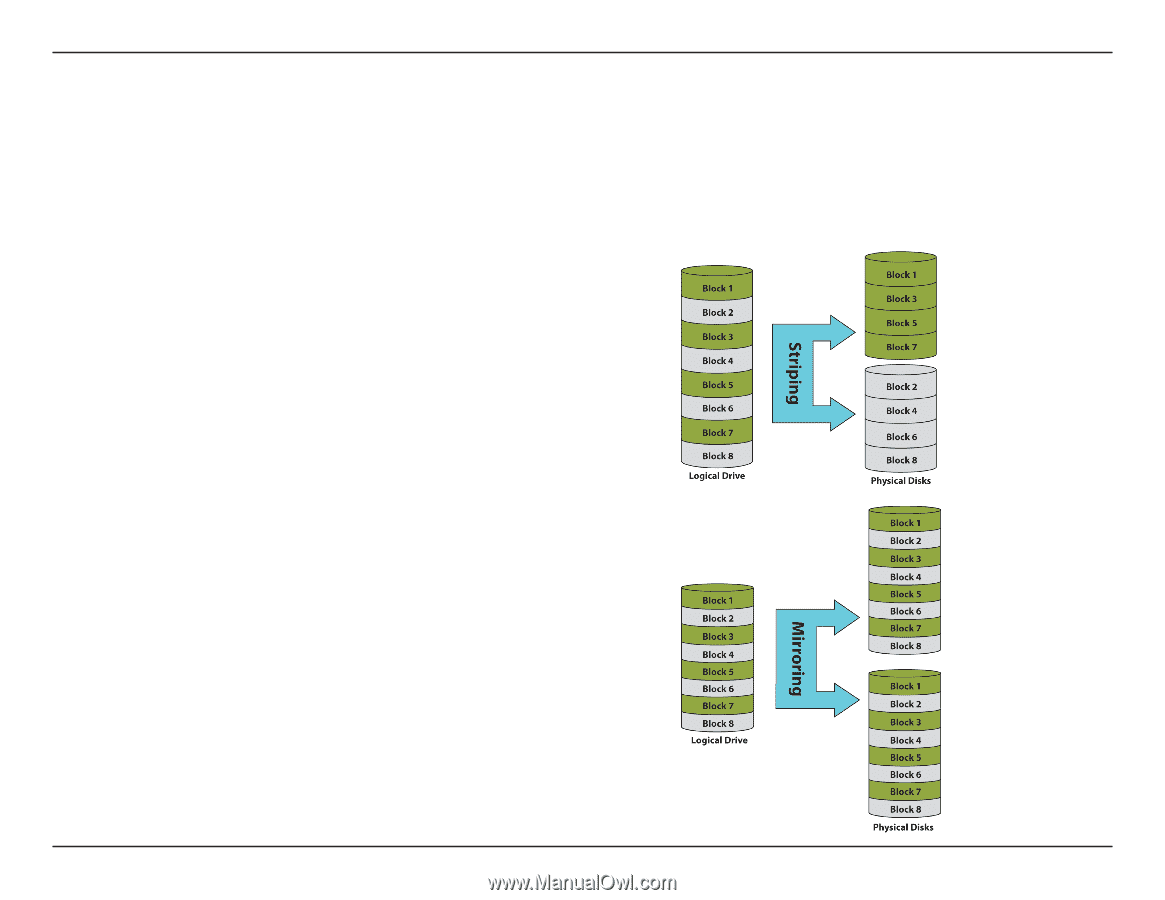
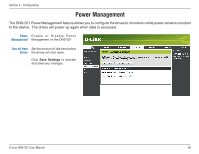
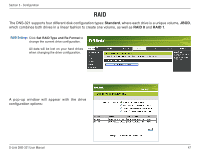
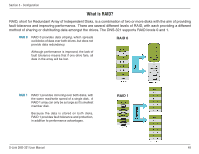
Section 3 - Configuration What is RAID? RAID, short for Redundant Array of Independent Disks, is a combination of two or more disks with the aim of providing fault tolerance and improving performance. There are several different levels of RAID, with each providing a different method of sharing or distributing data amongst the drives. The DNS-321 supports RAID levels 0 and 1. RAID 0 RAID 0 provides data striping, which spreads out blocks of data over both drives, but does not provide data redundancy. RAID 0 Although performance is improved, the lack of fault tolerance means that if one drive fails, all data in the array will be lost. RAID 1 RAID 1 provides mirroring over both disks, with the same read/write speed of a single disk. A RAID 1 array can only be as large as it's smallest member disk. Because the data is stored on both disks, RAID 1 provides fault tolerance and protection, in addition to performance advantages. RAID 1 D-Link DNS-321 User Manual 48