Dell PowerConnect 2848 User's Guide - Page 100
Configuring Advanced Port Based Authentication, Action on Single Host Violation - reset to defaults
 |
View all Dell PowerConnect 2848 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 100 highlights
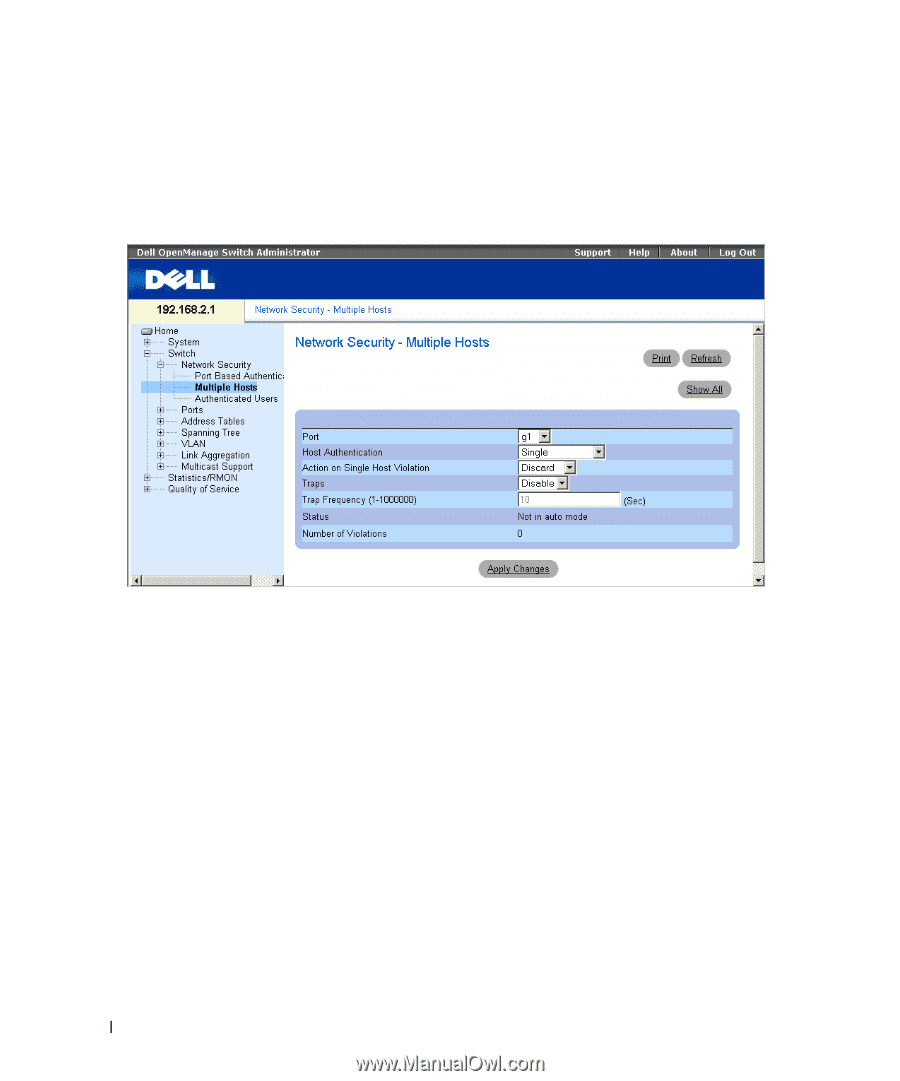
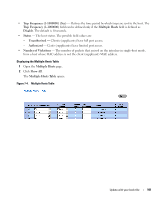
Configuring Advanced Port Based Authentication The Multiple Hosts page provides information for defining advanced port based authentication settings for specific ports. To open the Multiple Hosts, click Switch →Network Security → Multiple Hosts. Figure 7-3. Multiple Hosts • Port - The port number for which Advanced Port Based Authentication is enabled. • Host Authentication - Defines the host authentication type. The possible fields are: - Single - Enables a single authorized host for single-session access to the system. - Multiple Host - Enables a single host to authorize multiple hosts for single-session access to the system. - Multiple Session - Enables a single authorized host for multiple-session access to the system. • Action on Single Host Violation - Defines the action to be applied to packets arriving in single-host mode, from a host whose MAC address is not the client (supplicant) MAC address. The Action on Single Host Violation field can be defined only if the Multiple Hosts field is defined as Disable. The possible field values are: - Forward - Forwards the packets from an unknown source, however, the MAC address is not learned. - Discard - Discards the packets from any unlearned source. This is the default value. - Shutdown - Discards the packet from any unlearned source and locks the port. Ports remain locked until they are activated, or the device is reset. • Traps - Enables or disables sending traps to the host if a violation occurs. 100 Update with your book title