Dell PowerConnect 2848 User's Guide - Page 114
Configuring Address Tables, Viewing Dynamic Addresses
 |
View all Dell PowerConnect 2848 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 114 highlights
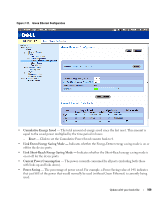
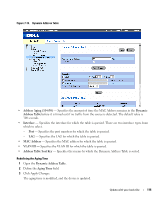
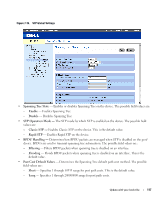
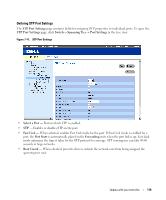
6 Click Apply Changes. The new source port is defined, and the device is updated. Deleting a Copy Port from a Port Mirroring Session 1 Open the Port Mirroring page. 2 Select the Remove check box. 3 Click Apply Changes. The selected port mirroring session is deleted, and the device is updated. Configuring Address Tables MAC addresses are stored in the Dynamic Address database. A packet addressed to a destination stored in the database is forwarded immediately to the port. The Dynamic Address Table can be sorted by interface, VLAN, and interface type. MAC addresses are dynamically learned as packets from sources arrive at the device. Addresses are associated with ports by learning the ports from the frame's source address. Frames addressed to a destination MAC address that is not associated with any port are flooded to all ports of the relevant VLAN. In order to prevent the bridging table from overflowing, dynamic MAC addresses, from which no traffic is seen for a certain period, are erased. To open the Address Tables page, click Switch→ Address Table in the tree view. Viewing Dynamic Addresses The Dynamic Address Table contains fields for querying information in the dynamic address table, including the interface type, MAC addresses, VLAN, and table sorting. Packets forwarded to an address stored in the address table are forwarded directly to those ports. The Dynamic Address Table also contains information about the aging time before a dynamic MAC address is erased, and includes parameters for querying and viewing the Dynamic Address list. The Current Address Table contains dynamic address parameters by which packets are directly forwarded to the ports. To open the Dynamic Address Table, click Switch→ Address Table→ Dynamic Addresses Table in the tree view. 114 Update with your book title