Dell PowerConnect 2848 User's Guide - Page 116
Configuring the Spanning Tree Protocol, Defining STP Global Settings
 |
View all Dell PowerConnect 2848 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 116 highlights
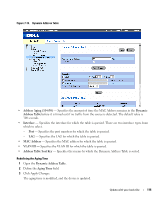
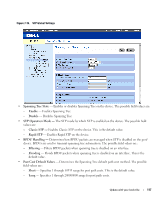
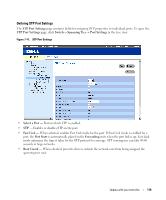
Querying the Dynamic Address Table 1 Open the Dynamic Address Table. 2 Define the parameter by which to query the Dynamic Address Table. Entries can be queried by Port, MAC Address, or VLAN ID. 3 Click Query. The Dynamic Address Table is queried. Sorting the Dynamic Address Table 1 Open the Dynamic Address Table. 2 From the Address Table Sort Key drop-down menu, select whether to sort addresses by address, VLAN ID, or interface. 3 Click Query. The Dynamic Address Table is sorted. Configuring the Spanning Tree Protocol Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) provides tree topography for any arrangement of bridges. STP also provides one path between end stations on a network, eliminating loops. Loops occur when alternate paths exist between hosts. Loops in an extended network can cause bridges to forward traffic indefinitely, resulting in increased traffic and reducing network efficiency. The devices support the following Spanning Tree protocols: • Classic STP - Provides a single path between end stations, avoiding and eliminating loops. For more information on configuring Classic STP, see "Defining STP Global Settings" on page 116. • Rapid STP - Detects and uses of network topologies that provide faster spanning tree convergence, without creating forwarding loops. For more information on configuring Rapid STP, see "Configuring Rapid Spanning Tree" on page 124. To open the Spanning Tree pages, click Switch→ Spanning Tree in the tree view. Defining STP Global Settings The STP Global Settings page contains parameters for enabling and configuring STP operation on the device. To open the STP Global Settings page, click Switch→ Spanning Tree → Global Settings in the tree view. 116 Update with your book title