Dell PowerConnect 2848 User's Guide - Page 126
Configuring VLANs, Defining VLAN Members
 |
View all Dell PowerConnect 2848 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 126 highlights
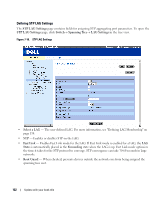
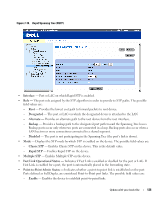
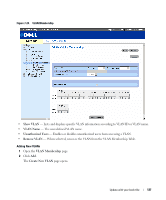
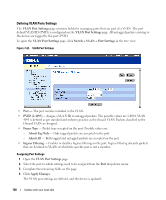
- Disable - Device establishes shared, half duplex links. - Auto - Device automatically determines the state. • Point-to-Point Operational Status - Displays the point-to-point operating state which depends on a link partner. • Activate Protocol Migration Test - Select to run a Protocol Migration Test. The test identifies the STP mode of the interface connected to the selected interface. - Checked - Runs a Protocol Migration Test on the interface after you click the Apply button. - Unchecked - Does not run a Protocol Migration Test. Enabling RSTP 1 Open the Rapid Spanning Tree (RSTP) page. 2 Define the Point-to-Point Admin, Point-to-Point Oper, and the Activate Protocol Migration fields. 3 Click Apply Changes. Rapid STP is enabled, and the device is updated. Configuring VLANs VLANs are logical subgroups of a Local Area Network (LAN) created via software rather than defining a hardware solution. VLANs combine user stations and network devices into a single domain regardless of the physical LAN segment to which they are attached. VLANs allow network traffic to flow more efficiently within subgroups. VLANs managed through software reduces the amount of time in which network changes are implemented. VLANs have no minimum number of ports, and can be created per device or any other logical connection combination, as VLANs are software based and not defined by physical attributes. VLANs function at Layer 2. Since VLANs isolate traffic within the VLAN, a Layer 3 router functioning router is needed to allows traffic flow between VLANs. Layer 3 routers identify segments and coordinate with VLANs. VLANs are broadcast and Multicast domains. Broadcast and Multicast traffic is transmitted only in the VLAN in which the traffic is generated. VLAN tagging provides a method of transferring VLAN information between VLAN groups. VLAN tagging attaches a tag to packet headers. The VLAN tag indicates to which VLAN the packet belongs. VLAN tags are attached to the packet by either the end station or by the network device. VLAN tags also contains VLAN network priority information. Combining VLANs and GVRP enables the automatic dispersal of VLAN information. To open the VLAN page, click Switch→ VLAN in the tree view. Defining VLAN Members The VLAN Membership page contains fields for defining port membership in the VLAN. The device supports 64 VLANs. All ports must have a defined PVID. If no other value is configured the default VLAN PVID is used. VLAN number 1 is the default VLAN, and cannot be deleted from the system. To open the VLAN Membership page, click Switch→ VLAN→ VLAN Membership in the tree view. 126 Update with your book title