Dell PowerConnect 2848 User's Guide - Page 134
Defining LAG Membership, Multicast Forwarding Support
 |
View all Dell PowerConnect 2848 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 134 highlights
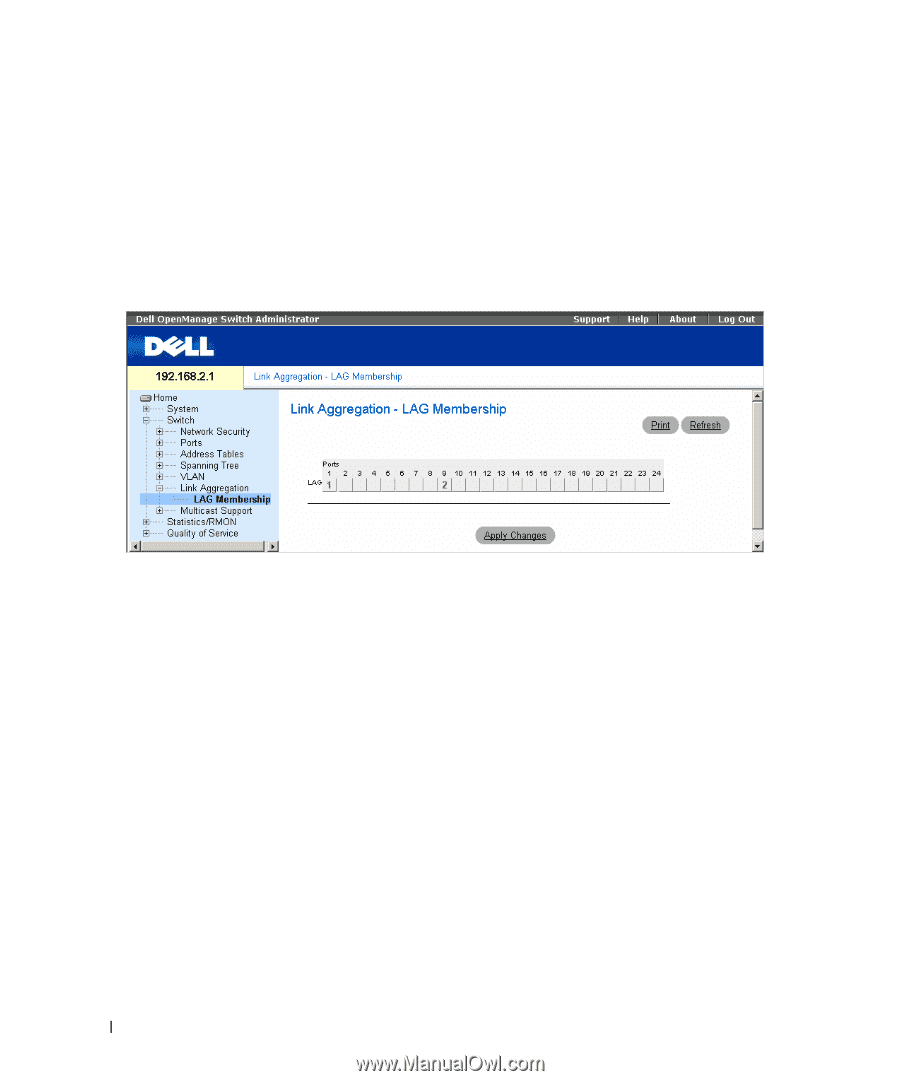
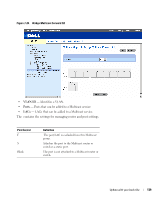
Defining LAG Membership The LAG Membership page contains fields for assigning ports to LAGs. LAGs can include up to 6 ports. When a port is added to a LAG, the port acquires the LAG's properties. If the port cannot be configured with the LAG properties, a trap is generated and the port operates with its default settings. The LAG Membership page contains fields for assigning ports to LAGs. To open the LAG Membership page, click Switch→ Link Aggregation→ LAG Membership in the tree view. Figure 7-25. LAG Membership • LAG - Adds a port to a LAG, and indicates the specific LAG to which the port belongs. Configuring a Port to a LAG 1 Open the LAG Membership page. 2 In the LAG row (the second row), toggle the button to a specific number to aggregate or remove the port to that LAG number. 3 Click Apply Changes. The port is added to the LAG, and the device is updated. Multicast Forwarding Support Multicast forwarding allows a single packet to be forwarded to multiple destinations. L2 Multicast service is based on L2 switch receiving a single packet addressed to a specific Multicast address. Multicast forwarding creates copies of the packet, and transmits the packets to the relevant ports. Filtering L2 Multicast packets enables forwarding of Layer 2 packets to interfaces. If Multicast filtering is disabled, Multicast packets are flooded to all relevant ports. Forwarding L2 Multicast packets is enabled by default, and not configurable. The system supports Multicast filtering for 64 Multicast groups. To open the Multicast Support page, click Switch→ Multicast Support in the tree view. 134 Update with your book title