Dell PowerConnect 2848 User's Guide - Page 135
Defining Multicast Global Parameters, Switch, Multicast, Support, Global Parameters
 |
View all Dell PowerConnect 2848 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 135 highlights
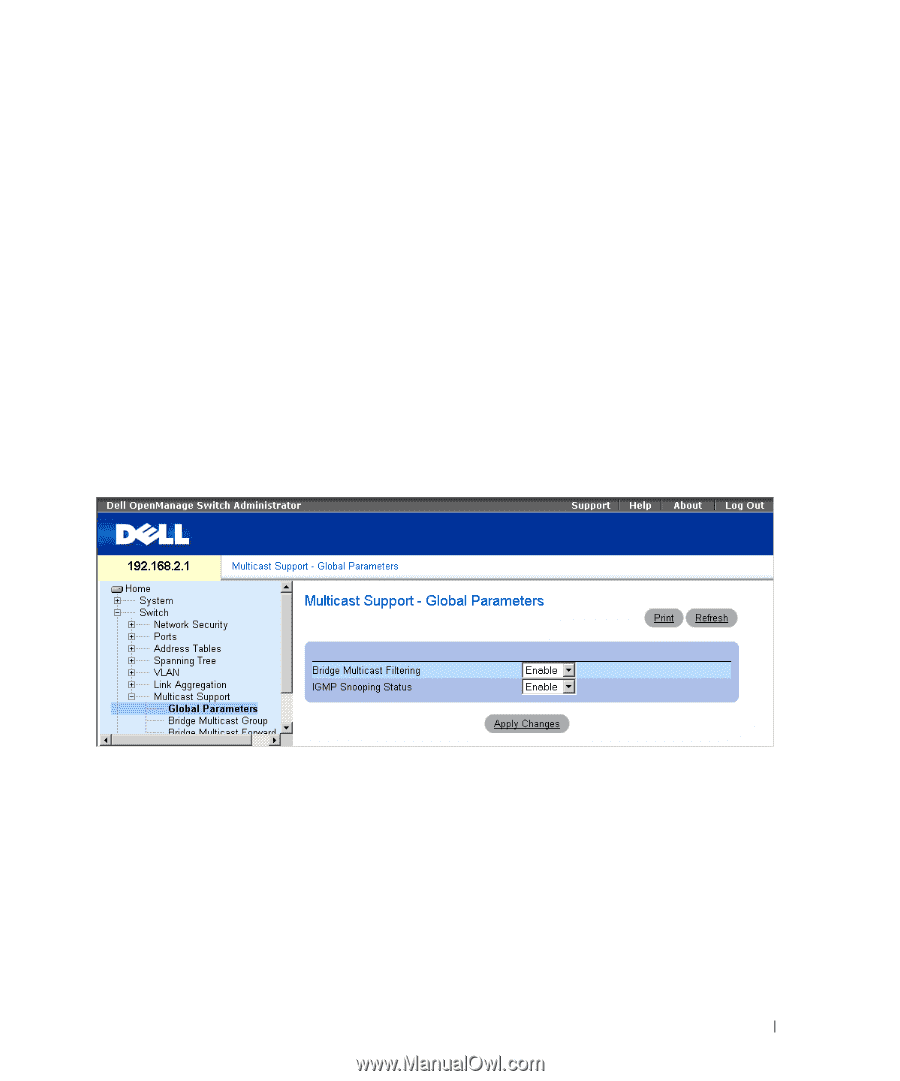
Defining Multicast Global Parameters Layer 2 switching forwards Multicast packets to all relevant VLAN ports by default, treating the packet as a Multicast transmission. While this is functional, in the sense that all relevant ports/nodes receive a copy of the frame, it is potentially wasteful as ports/nodes may receive irrelevant frames only needed by a subset of the ports of that VLAN. Multicast forwarding filters enable forwarding of Layer 2 packets to port subsets, defined in the Multicast filter database. When IGMP snooping is enabled globally, the switching ASIC is programmed to forward all IGMP packets to the CPU. The CPU analyzes the incoming packets and determines which ports are to join which Multicast groups, which ports have Multicast routers generating IGMP queries, and what routing protocols are forwarding packets and Multicast traffic. Ports requesting to join a specific Multicast group issues an IGMP report specifying that Multicast group. This results in the creation of the Multicast filtering database. The Multicast Global Parameters page contains fields for enabling Bridge Multicast Filtering and IGMP Snooping on the device. To open the Multicast Global Parameters page, click Switch→ Multicast Support→ Global Parameters in the tree view. Figure 7-26. Multicast Global Parameters • Bridge Multicast Filtering - Enables or disables bridge Multicast filtering. Disabled is the default value. IGMP Snooping can be enabled only if Bridge Multicast Filtering is enabled. • IGMP Snooping Status - Enables or disables IGMP Snooping on the device. Disabled is the default value. Enabling Bridge Multicast Filtering on the Device 1 Open the Multicast Global Parameters page. 2 Select Enable in the Bridge Multicast Filtering field. 3 Click Apply Changes. Bridge Multicast is enabled on the device. Update with your book title 135