Dell PowerConnect 2848 User's Guide - Page 84
Configuring DHCP Properties, Static allocation, Permanent allocation, DHCP Server, System
 |
View all Dell PowerConnect 2848 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 84 highlights
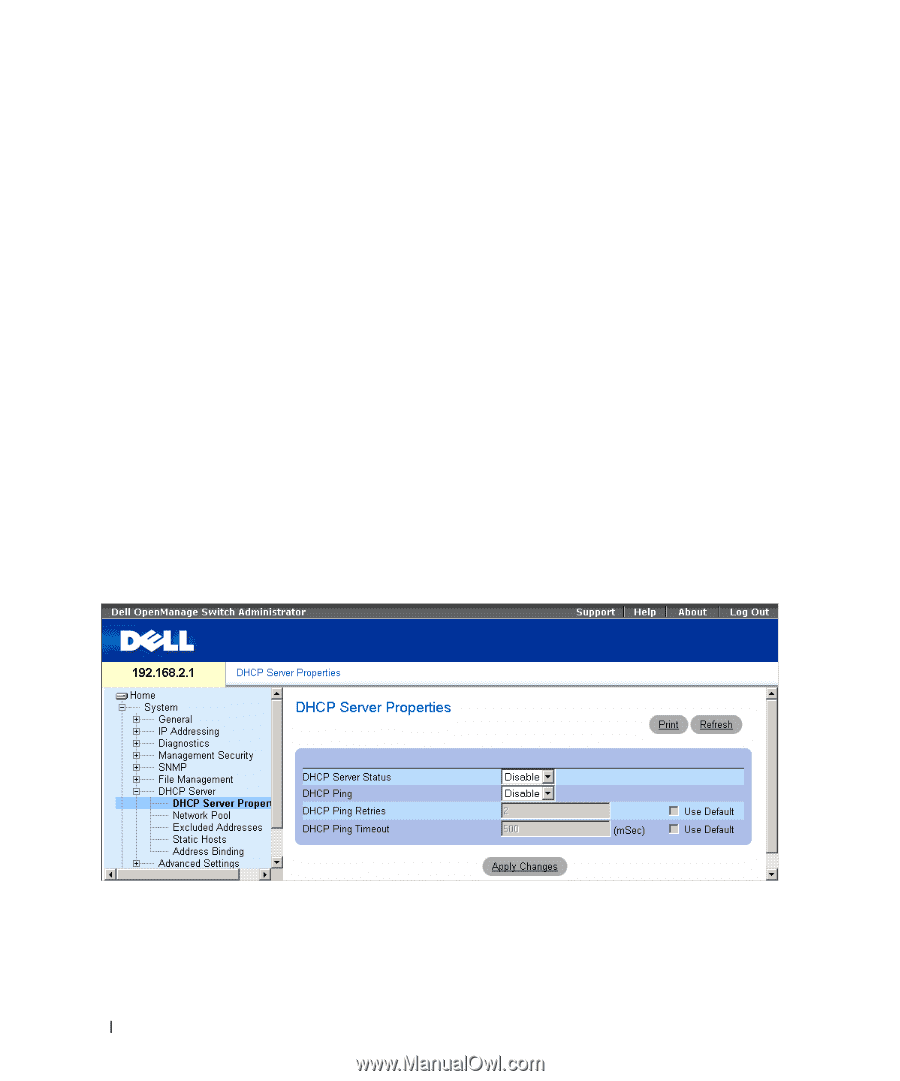
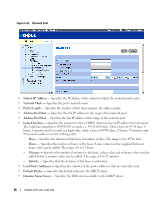
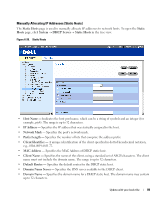
The DHCP server uses a defined pool of IP addresses (user-defined) from which it allocates IP addresses to DHCP clients. The DHCP server can allocate IP addresses in three configuration modes: • Static allocation - The network administrator maps the hardware address of a host to an IP address on the DHCP server. • Permanent allocation - An IP address received through a standard request-reply mechanism is owned by a client permanently (unless changes in the network environment/connections take place, for any reason). • Dynamic allocation - A network device obtains a leased IP address for a specified period of time. The IP address is revoked at the end of this period and the switch must request another IP address. This section contains information for configuring a DHCP server on a DHCP-server-enabled switch. To open the DHCP Server page, click System → DHCP Server in the tree view. Configuring DHCP Properties The DHCP Server Properties page contains fields for enabling the DHCP server and configuring pinging capability. The DHCP Server pings a pool address before assigning this address to a requesting client. If the ping is unanswered, the DHCP Server assumes (with a high probaility) that the address is not in use and assigns the address to the requesting client. To open the DHCP Server Properties page, click System → DHCP Server → DHCP Server Properties in the tree view. Figure 6-24. DHCP Server Properties • DHCP Server Status - Indicates if the DHCP server is enabled. The possible field values are: - Enable - Enables the DHCP server. - Disable - Disables the DHCP server. This is the default value. 84 Update with your book title