Dell V313W User's Guide - Page 81
How do I find the MAC address?, What is an IP address?, Media Access Control
 |
UPC - 884116016519
View all Dell V313W manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 81 highlights
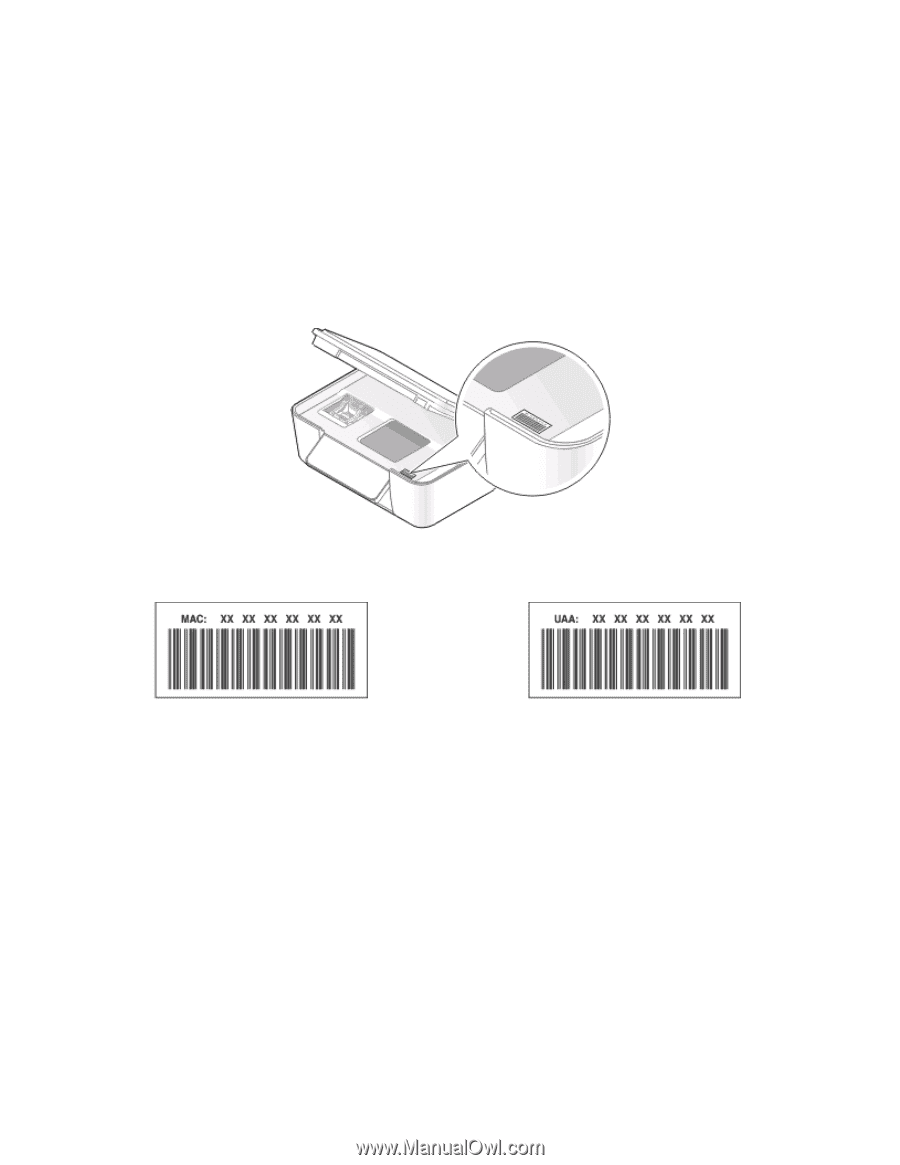
Routers with security capabilities may allow filtering of MAC addresses on networks. This allows a managed list of devices to access the network, identified by their MAC addresses, as well as prevent access from unwanted devices. If your network uses MAC address filtering, then be sure to add the MAC address of the printer to the list of allowed devices. How do I find the MAC address? Most network equipment has a unique hardware identification number to distinguish it from other devices on the network. This is called the Media Access Control (MAC) address. When installing the printer on a network, make sure you select the printer with the correct MAC address. The MAC address label is located inside the printer. The MAC address of the internal print server is a series of letters and numbers. Other devices sometimes use a type of MAC address called Universally Administered Address (UAA). Note: A list of MAC addresses can be set on an access point (router) so that only devices with matching MAC addresses are allowed to operate on the network. This is called MAC filtering. If MAC filtering is enabled in your access point and you want to add a printer to your network, then the MAC address of the printer must be included in the MAC filter list. What is an IP address? An IP address is a unique number used by devices (such as a wireless printer, computer, or wireless access point) on an IP network to locate and communicate with each other. Devices on an IP network can communicate with each other only if they have unique and valid IP addresses. A unique IP address means no two devices on the same network have the same IP address. An IP address is a group of four numbers separated by periods. An example of an IP address is 192.168.100.110. Networking 81