Epson Perfection 1640SU Office Technical Brief (Scanners)
Epson Perfection 1640SU Office Manual
 |
View all Epson Perfection 1640SU Office manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Epson Perfection 1640SU Office manual content summary:
- Epson Perfection 1640SU Office | Technical Brief (Scanners) - Page 1
to Digital converter (ADC); Epson scanners have optimum performance for minimal noise and tight color registration. Type of focus method Optic system Color vs. monochrome CCD The Epson Expression® and GT series scanners are Epson's professional series scanners designed for excellence with respect - Epson Perfection 1640SU Office | Technical Brief (Scanners) - Page 2
the number of bits of data captured for each picture element (pixel). Each pixel can have two states (On or Off); therefore the number of colors or gray scales that a scanner can recognize is computed by taking the pizel depth as an exponent of two. The following charts lists the number of - Epson Perfection 1640SU Office | Technical Brief (Scanners) - Page 3
Image Quality-Pixel depth (cont.) All Epson scanners have a 42-bit or 48-bit color depth. but some of the models support 24-bit external color depth, which is the data that is sent from the scanner to the computer. Here are the differences between output color depth: Key Differences 42-bit, or 48- - Epson Perfection 1640SU Office | Technical Brief (Scanners) - Page 4
System deliver scanned images with: Smooth gradations Accurate colors Smooth edges and minimal color fringing Greater detail in shadows Greater detail in highlights Sharp image quality without distortion 1. Hardware components: Epson scanners use a precise scan carriage with better motors to - Epson Perfection 1640SU Office | Technical Brief (Scanners) - Page 5
On Off On Off On Off Some competitive models lower resolution by turning off some pixels to capture less image data. 300 dpi Image Quality-Color CCD All Epson scanners use a color CCD which uses a single white light source, instead of a monochrome CCD and three light sources. The - Epson Perfection 1640SU Office | Technical Brief (Scanners) - Page 6
Perfection and GT series scanners use a fixed focus optics system. The newest Epson scanners have a fixed focal point just above the surface of the glass for optimized film scanning. 2. AutoFocus optics system: Epson highest-end graphic Epson automatic/manual focus arts scanners use an AutoFocus optics - Epson Perfection 1640SU Office | Technical Brief (Scanners) - Page 7
Lens System offers two lenses for two different resolutions. High Resolution lens Some Epson Perfection scanners offers 4800 dpi optical resolution with the High Resolution lens. Document (8.5") Film Area Guide (8") High resolution lens Super Resolution lens For a higher resolution of 6400 dpi - Epson Perfection 1640SU Office | Technical Brief (Scanners) - Page 8
unit attached, Epson scanners can scan color negatives (such as 35mm negative strips) and convert them directly to positive images. Some other scanners can only scan positive transparent media, such as color transparencies and slides. Negative Select and define frames in the scanner driver, and - Epson Perfection 1640SU Office | Technical Brief (Scanners) - Page 9
on the network. Install Epson Scan Server (Windows only) on that computer. Install the Epson TWAIN Pro Network scanner driver on all computers that will access the scanner over the network. Flexibility-Epson Scan with Epson Easy Photo Fix™ Scanning Software Epson Easy Photo Fix technology is - Epson Perfection 1640SU Office | Technical Brief (Scanners) - Page 10
software to remove dust and scratches on film and remove tears, folds, creases, and deep scratches on photos. This feature is not available on all Epson scanners. Scratch Fold Color photo before DIGITAL ICE Color photo after DIGITAL ICE Scanner Technical Brief-Page 10 6/07 - Epson Perfection 1640SU Office | Technical Brief (Scanners) - Page 11
from film not supported by DIGITAL ICE Epson America, Inc. All other products and brands are trademarks and/or registered trademarks of their respective companies. Epson disclaims any and all rights in those marks. DIGITAL ICE is a trademark of Eastman Kodak Company. ©2007 Epson America, Inc. Scanner

Scanner Technical Brief—Page 1
6/07
This technical brief provides detailed information on the Image Quality, Performance, and Flexibility of Epson
Scanners.
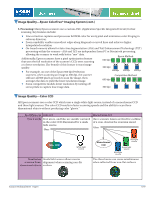
Image Quality—Factors affecting image quality
When comparing scanners, hardware resolution and color pixel depth are two features often used to gauge
image quality. These two features are important, but there are a number of factors that determine image
quality in a scanner, such as the following: (Many of these elements will be discussed in detail in upcoming
sections of this document.)
The Epson Expression
®
and GT series scanners are Epson’s professional series scanners designed for excel-
lence with respect to image quality, speed, usability, versatility, and durability. These scanners include the
highest quality components.
Precision stepper motor
for high quality sub-scan
resolution
Dynamic range control
Type of lamp system used
Optic system
Optical resolution and
color bit depth
Quality of the Analog to Digital con-
verter (ADC); Epson scanners have
optimum performance for minimal
noise and tight color registration.
Type of focus method
Color vs. monochrome CCD
The Epson Perfection
®
series scanners are designed for home and entry-level corporate and graphics arts
users, and are designed with the highest quality components in their price class.
Image Quality—Resolution
A scanner’s resolution determines the amount of data that is read by the scanner. As resolution increases, so
does the file size. Resolution is measured in a variety of ways.
1. Optical resolution:
This is the actual number of pixels read by the CCD (Charge Coupled Device), which
measures the intensity of the light that is reflected from the image to be scanned, and converts it to an
analog voltage. If a scanner has a resolution of 600 x 2400 dpi, its optical resolution is 600 dpi, which
means that it can resolve 600 bits of data per inch.
2. Hardware resolution:
Using a precision stepper motor to double-step or
quadruple-step the carriage, the scanner’s sub-scanner resolution can be
increased. For example, a scanner can have an optical resolution of 1200
dpi, but a hardware resolution of 1200 x 2400 dpi (because it double-steps
the carriage to increase the vertical resolution).
2400 dpi
1200 dpi