HP 4200n HP Jetdirect Print Servers - Administrator Guide - Page 248
Subnets, Subnet Mask
 |
UPC - 808736313971
View all HP 4200n manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 248 highlights
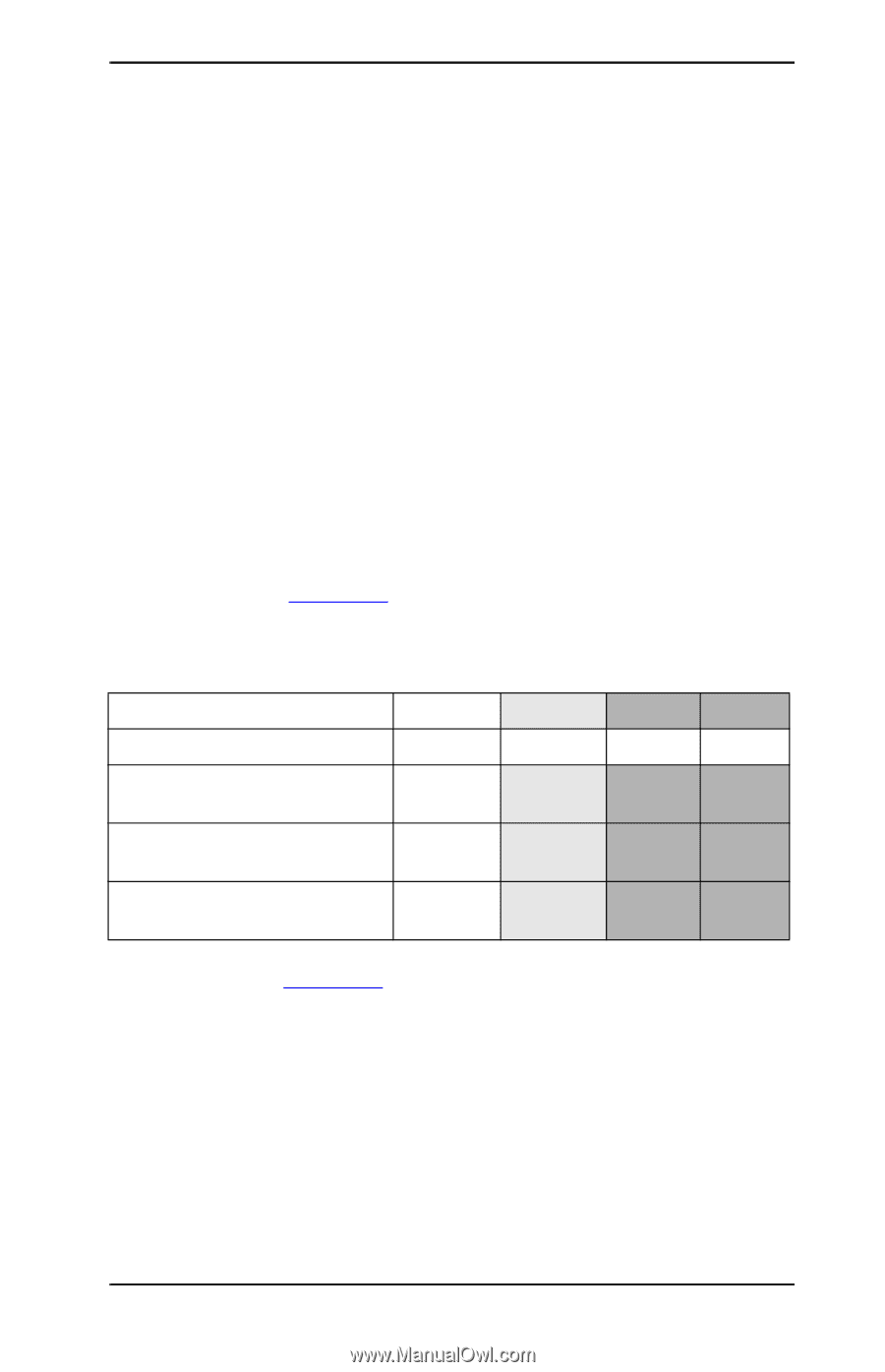
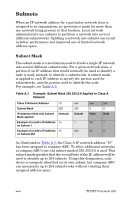
Subnets When an IP network address for a particular network class is assigned to an organization, no provision is made for more than one network being present at that location. Local network administrators use subnets to partition a network into several different subnetworks. Splitting a network into subnets can result in better performance and improved use of limited network address space. Subnet Mask The subnet mask is a mechanism used to divide a single IP network into several different subnetworks. For a given network class, a portion of an IP address that would normally be used to identify a node is used, instead, to identify a subnetwork. A subnet mask is applied to each IP address to specify the portion used for subnetworks, and the portion used to identify the node. For example, see Table A.3. Table A.3 Example: Subnet Mask 255.255.0.0 Applied to Class A Network Class A Network Address 15 Subnet Mask 255 IP Address fields with Subnet Network Mask applied Example of a node's IP Address 15 on Subnet 1 Example of a node's IP Address 15 on Subnet 254 xxx 255 Subnet 1 254 xxx 0 Host 25 64 xxx 0 Host 7 2 As illustrated in Table A.3, the Class A IP network address "15" has been assigned to company ABC. To allow additional networks at company ABC's site, the subnet mask of 255.255.0.0 is used. This subnet mask specifies that the second byte of the IP address will be used to identify up to 254 subnets. Using this designation, each device is uniquely identified on its own subnet, but company ABC can incorporate up to 254 subnetworks without violating their assigned address space. NWW TCP/IP Overview 248