HP AM866A Brocade Troubleshooting and Diagnostics Guide v6.1.0 (53-1000853-01, - Page 33
Link issues, Connection problems, Checking the logical connection
 |
UPC - 884420064602
View all HP AM866A manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 33 highlights
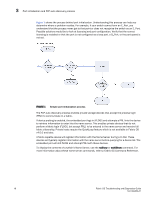
Link issues 3 Link issues Symptom LEDs are flashing. Probable cause and recommended action Depending on the rate of the flash and the color of the LED this could mean several things. To determine what is happening on either your port status LED or power status LED, refer to that switch's model hardware reference manual. There is a table that describes the LEDs purpose and explains the current behavior as well as provides suggested resolutions. Symptom LEDs are steady. Probable cause and recommended action The color of the LED is important in this instance. To determine what is happening on either your port status LED or power status LED, refer to that switch's model hardware reference manual. There is a table that describes the LEDs purpose and explains the current behavior as well as provides suggested resolutions. Symptom No light from the LEDs. Probable cause and recommended action If there is no light coming from the LED, then no signal is being detected. Check your cable and SFP to determine the physical fault. Symptom EX_Port does not form. Probable cause and recommended action This usually happens when the fabric parameters are set up correctly for the EX_Port. A common parameter to check is the use of the World Wide Node Name (WWNN) instead of the port World Wide Name (pWWN). To fix this problem use the pWWN instead. Connection problems If a host is unable to detect its target, for example, a storage or tape device, you should begin troubleshooting the problem at the switch. Determine if the problem is the target or the host, then continue to divide the suspected problem-path in half until you can pinpoint the problem. One of the most common solutions is zoning. Verify that the host and target are in the same zone. For more information on zoning, refer to Chapter 8, "Zone Issues". Checking the logical connection 1. Enter the switchShow command. 2. Review the output from the command and determine if the device successfully logged into the switch. • A device that is logically connected to the switch is registered as an F_, L_, E_, EX_, VE_, VEX_, or N_Port. Fabric OS Troubleshooting and Diagnostics Guide 19 53-1000853-01