HP AM866A Brocade Troubleshooting and Diagnostics Guide v6.1.0 (53-1000853-01, - Page 38
Marginal links, Troubleshooting a marginal link
 |
UPC - 884420064602
View all HP AM866A manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 38 highlights
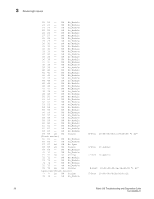
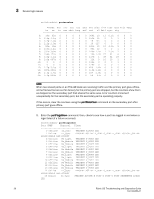
3 Marginal links TABLE 4 Output G_Port L_Port SwitchShow output and suggested action (Continued) Suggested action The port has not come up as an E_Port or F_Port. Check the output from portLogShow or PortLogDump commands and identify the link initialization stage where the initialization procedure went wrong. If the opposite side is not a loop device, the link has come up in a wrong mode. Check the output from portLogShow or PortLogDump commands and identify the link initialization stage where the initialization procedure went wrong. NOTE If you are unable to read a portlog dump, contact your switch support provider for assistance. Marginal links A marginal link involves the connection between the switch and the edge device. Isolating the exact cause of a marginal link involves analyzing and testing many of the components that make up the link (including the switch port, switch SFP, cable, edge device, and edge device SFP). Troubleshooting a marginal link 1. Enter the portErrShow command. 2. Determine whether there is a relatively high number of errors (such as CRC errors or ENC_OUT errors), or if there are a steadily increasing number of errors to confirm a marginal link. 3. If you suspect a marginal link, isolate the areas by moving the suspected marginal port cable to a different port on the switch. Reseating of SFPs may also cure marginal port problems. If the problem stops or goes away, the switch port or the SFP is marginal (proceed to step 4) If the problem does not stop or go away, see step 7. 4. Replace the SFP on the marginal port. 5. Run the portLoopbackTest on the marginal port. You will need an adapter to run the loopback test for the SFP. Otherwise, run the test on the marginal port using the loopback mode lb=5. See the Fabric OS Command Reference for additional information on this command. TABLE 5 Loopback modes Loopback mode Description 1 Port Loopback (loopback plugs) 2 External Serializer/Deserializer (SerDes) loopback 5 Internal (parallel) loopback (indicates no external equipment) 7 Back-end bypass and port loopback 8 Back-end bypass and SerDes loopback 9 Back-end bypass and internal loopback 6. Check the results of the loopback test and proceed as follows: • If the loopback test failed, the port is bad. Replace the port blade or switch. 24 Fabric OS Troubleshooting and Diagnostics Guide 53-1000853-01