HP Dl180 Drive technology overview
HP Dl180 - G6 E5504 2X2gb 4Lff Svr Manual
 |
UPC - 883585990917
View all HP Dl180 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
HP Dl180 manual content summary:
- HP Dl180 | Drive technology overview - Page 1
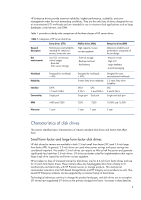
server disk drives ...2 Characteristics of disk drives ...3 Small form factor and large form factor disk drives 3 Disk drive capacity...4 Disk Improved performance and reliability with RAID 9 Advanced controllers ...9 Solid state drives for servers...9 HP solid state drive reliability requirements - HP Dl180 | Drive technology overview - Page 2
or as boot disks for entry-level servers. HP Midline drives provide larger capacity and greater reliability than Entry drives. HP Midline drives have improved resistance to rotational and operational vibration, so they are better suited than Entry drives for use in multi-drive configurations. For - HP Dl180 | Drive technology overview - Page 3
family to fit mechanically and electrically with HP ProLiant servers or storage products. This mechanical commonality extends to most SAS-based StorageWorks and HP Integrity server products as well. Thus, mixed HP Enterprise solutions can be supported by a common family of hard drives. Technological - HP Dl180 | Drive technology overview - Page 4
drives, combined with their lower power and smaller size, have hastened this transition. By the end of 2010, all new enterprise class drives and all new 10k and 15k RPM drives will be SFF. HP expects to continue to develop 3.5-inch midline and entry class drives. Disk drive capacity The capacity of - HP Dl180 | Drive technology overview - Page 5
read/write operation. These strategies seek to effectively decouple the logical and physical operations of the disk. Increasingly sophisticated approaches become practical as the embedded processing power and memory incorporated into the drive increases. There are several approaches that can be used - HP Dl180 | Drive technology overview - Page 6
's quality performance through the HP configuration pilot. Disk drive products that pass the extensive HP qualification process proceed into the HP continuous improvement/disk drive performance monitoring phase during volume production. This phase includes three main areas of focus: Validate that - HP Dl180 | Drive technology overview - Page 7
HP option kitting configuration sites. Product quality data is reviewed on a daily, weekly, and monthly basis. Interconnect technology Various interconnect technologies are used to connect one or more disk standard servers 2nd Gen. swap support yes yes yes Drive ID Drives supported Optional - HP Dl180 | Drive technology overview - Page 8
were first introduced with HP ProLiant G6 servers in 2009. The SAS-2 interface will support SAS and SATA drives; however, the 6 Gb/s link speed is only achieved using new SAS-2 compliant disk drives. SAS-2 also supports SAS expanders to create a SAS fabric supporting large numbers of drives - HP Dl180 | Drive technology overview - Page 9
and SCSI interfaces. For further details, see the technology brief entitled "HP Smart Array Controller Technology," at http://h20000.www2.hp.com/bc/docs/support/SupportManual/c00687518/c00687518.pdf. Solid state drives for servers Solid state drives represent a new type of storage technology that is - HP Dl180 | Drive technology overview - Page 10
memory controllers, HP has been able to develop solid state drives that can meet the performance and reliability requirements for use in server environments. Figure 1. HP flash array itself. All HP ProLiant SSDs feature power loss protection, which ensures that in the case of power loss to the drive - HP Dl180 | Drive technology overview - Page 11
disk drives. SSDs are differentiated primarily by the read/write workload levels that they are able to support and their endurance, or expected service life. The current 2nd generation HP service life. Unconstrained workloads < 1 year Usage environment Interface Power Operating Environment Boot - HP Dl180 | Drive technology overview - Page 12
and vibration (up to 1000G) Environments requiring drives with lower power consumption (2 watts) HP SSDs are designed for an operational life of over three years, the typical service life for a new server. The NAND memory used in SSDs has a relatively well understood lifespan that is primarily - HP Dl180 | Drive technology overview - Page 13
http://h20000.www2.hp.com/bc/docs/support/Support Manual/c00301688/c00301688.pdf http://h20000.www2.hp.com/bc/docs/support/Support Manual/c01613420/c01613420.pdf Technology brief Solid state drive technology for ProLiant servers http://h20000.www2.hp.com/bc/docs/support/SupportManu al/c01580706

1
Abstract
..............................................................................................................................................
2
Introduction
.........................................................................................................................................
2
Categories of server disk drives
.............................................................................................................
2
Characteristics of disk drives
.................................................................................................................
3
Small form factor and large form factor disk drives
..............................................................................
3
Disk drive capacity
...........................................................................................................................
4
Disk drive performance
.....................................................................................................................
4
Reliability
........................................................................................................................................
5
Drive qualification process
....................................................................................................................
6
Interconnect technology
........................................................................................................................
7
Serial Attached SCSI (SAS)
...............................................................................................................
7
SAS-2
.............................................................................................................................................
8
Second generation Serial ATA (SATA)
................................................................................................
8
Interconnect bandwidths and drive throughput
.....................................................................................
8
Improved performance and reliability with RAID
......................................................................................
9
Advanced controllers
...........................................................................................................................
9
Solid state drives for servers
..................................................................................................................
9
HP solid state drive reliability requirements
........................................................................................
10
NAND over provisioning and wear-levelling
..................................................................................
10
Power loss protection
..................................................................................................................
10
Value, mainstream and performance SSDs
........................................................................................
11
SSD performance
...........................................................................................................................
12
Conclusion
........................................................................................................................................
12
For more information
..........................................................................................................................
13
Call to action
....................................................................................................................................
13
Drive technology overview
technology brief, 3
rd
edition