HP LaserJet 9040/9050 Service Manual - Page 38
Storing print media, Embossed media, Media that contains cutouts or perforations
 |
View all HP LaserJet 9040/9050 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 38 highlights
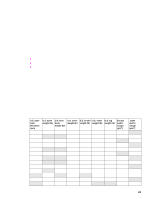
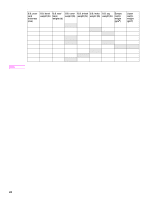
Embossed media Embossed media is not recommended for use in HP LaserJet printers. Media is embossed by stamping an image into the media by compressing the media fibers together at approximately 200°C (392°F), and sometimes by applying a thin metal foil to the surface. The printer fusing process can loosen the foil, and loose foil can interfere with the mechanical and electronic operation of the printer. Embossed paper, with or without foil, can also cause multifeed jams. Multiple embossed print media sheets tend to stick to one another. Media that contains cutouts or perforations Avoid media that contains cutouts or perforations for these reasons: z Cut fibers absorb more moisture and can increase waviness and media curl. This decreases the print quality near the cutout or perforated area. z Cutting knives leave a sharp edge on the cutout or perforation. If the sharp edge is facing the print cartridge drum during printing, it can scratch the drum surface. z If printing occurs over a cutout hole, the transfer roller is contaminated with unused toner, creating light streaks on the paper. Chemically treated media Coatings such as lacquers, polymers, laminations, or other chemicals protect the paper, but can cause problems in the fuser and transfer areas of HP LaserJet printers. The surface resistivity and moisture content can be greatly altered, resulting in print-quality problems. Hard surface coatings increase wear on the rollers and media guides. All chemically treated media must meet HP specifications for fusing compatibility. Synthetic media Synthetic media (those manufactured from man-made fibers) do not perform as well as bond media in any printer, especially HP LaserJet printers. All synthetic media must meet HP specifications, especially for caliper and fusing compatibility. Coated media Do not use coated media. Most coated media does not meet the specifications for fusing compatibility and other specifications for HP LaserJet printers. Other special media z Odd sizes: check minimum and maximum supported sizes in chapter 2. z Carbonless media: carbonless media (NCR) is not supported by HP LaserJet printers. z Recycled media: choose recycled media that meets Hewlett-Packard specifications. Note that recycled media might not be as bright as indicated in the specifications. HP recommends that recycled media contain no more than 5% groundwood. See "Paper weight equivalence table" on page 23. Storing print media Ideally, the printing and media storage environment should be at or near room temperature, and should not be too dry or too humid. Remember that paper is hygroscopic; it absorbs and loses moisture rapidly. Heat works with humidity to damage paper. Heat causes the moisture in paper to evaporate, while cold causes it to condense on the sheets. Heating systems and air conditioners remove most of the humidity from a room. As a package is opened and used the paper is used, it loses moisture, causing 22 Chapter 2 Product requirements