HP Officejet 7300 Network Guide - Page 27
<number>, Not Applicable, Open System, Shared Key, WPA-PSK, bit WEP, WPA-AES, WPA-TKIP - wireless
 |
View all HP Officejet 7300 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 27 highlights
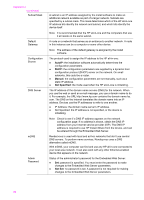
Appendix a (continued) Authentication type Encryption number. Value is from 1 to 14; countries/regions might limit the range of approved channels. ● : value ranging from 1 to 14, depending on country/region. ● None: no channel is in use. ● Not Applicable: the WLAN is disabled or this parameter does not apply to this network type. Note In ad hoc mode, if you are not able to receive or transmit data between your computer and the HP all-in-one, make sure that you are using the same communication channel on your computer and the HP all-in-one. In infrastructure mode, the channel is dictated by the access point. Type of authentication in use: ● None: no authentication in use. ● Open System (ad hoc and infrastructure): no authentication. ● Shared Key (infrastructure only): WEP key is required. ● WPA-PSK (infrastructure only): WPA with Pre-Shared Key. ● Not applicable: this parameter does not apply to this network type. Authentication verifies the identity of a user or device before granting access to the network, making it more difficult for unauthorized users to get at network resources. This security method is common on wireless networks. A network using Open System authentication does not screen network users based on their identities. Any wireless user can have access from the network. However, such a network might use WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy) encryption to provide a first level of security against casual eavesdroppers. A network using Shared Key authentication provides increased security by requiring users or devices to identify themselves with a static key (a hexadecimal or alphanumeric string). Every user or device on the network shares the same key. WEP encryption is used along with shared key authentication, using the same key for both authentication and encryption. A network using server-based (WPA-PSK) authentication provides significantly stronger security, and is supported in most wireless access points and wireless routers. The access point or router verifies the identity of a user or device requesting access to the network before granting that access. Several different authentication protocols might be used on an authentication server. Note Shared key and WPA-PSK authentication can only be entered through the Embedded Web Server. The type of encryption in use on the network: ● None: no encryption is in use. ● 64-bit WEP: a 5-character or 10-hex-digit WEP key is in use. ● 128-bit WEP: a 13-character or 26-hex-digit WEP key is in use. ● WPA-AES: Advanced Encryption Standard encryption is in use. This is an encryption algorithm for securing sensitive but unclassified material by US Government agencies. ● WPA-TKIP: Temporal Key Integrity Protocol, an advanced encryption protocol, is in use. 24