HP Pro 3500 GPT Hard Disk Drives for HP Business Desktops
HP Pro 3500 Manual
 |
View all HP Pro 3500 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
HP Pro 3500 manual content summary:
- HP Pro 3500 | GPT Hard Disk Drives for HP Business Desktops - Page 1
HP Desktops April 2011 Table of Contents: Abstract ...1 Why GPT?...1 GPT vs MBR ...2 Bootable vs Data Drives and UEFI BIOS 4 OS Support ...6 Storage Driver Support 6 Imaging Tool Support for GPT 7 Drive Encryption 7 Summary ...8 For more information 8 Abstract In order to be used in a computer - HP Pro 3500 | GPT Hard Disk Drives for HP Business Desktops - Page 2
(UEFI) specification, allows for BIOS and UEFI-aware OS. GPT vs MBR There are a number of differences between MBR and GPT. Some of the key differences include the following: • MBR only supports 4 primary partition table entries while GPT supports 128 primary partitions with current Microsoft Windows - HP Pro 3500 | GPT Hard Disk Drives for HP Business Desktops - Page 3
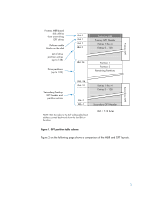
Primary GPT Protects MBR-based disk utilities from overwriting GPT drives Defines usable blocks on the disk List of drive partition entries (up to 128) Drive partitions (up to 128) LBA 0 LBA 1 LBA 2 LBA 3 Protective MBR Primary GPT Header Entries 1 thru 4 Entries 5 - 128 LBA 34 Partition 1 - HP Pro 3500 | GPT Hard Disk Drives for HP Business Desktops - Page 4
the boot information on a GPT drive. In addition, the system must also have a "UEFI aware" OS such as Microsoft Windows 7 ™64-bit. For selected desktops, HP implements the Type 0 BIOS Information data structure (as described in version 2.7 of the SMBIOS specification) to indicate UEFI BIOS support - HP Pro 3500 | GPT Hard Disk Drives for HP Business Desktops - Page 5
Extension Byte 2 Bit Position Description 0 When set, BIOS boot specification is supported 1 When set, function key-initiated Network Service boot is supported. When function key-initiated Network Service boot is not supported, a network option ROM may choose to offer this functionality on - HP Pro 3500 | GPT Hard Disk Drives for HP Business Desktops - Page 6
64-bit Yes (requires UEFI BIOS) Yes Windows Vista™ SP1 32-bit No Yes Linux™ No direct support from HP No direct support from HP Storage Driver Support Since GPT drives have capacities beyond 2.2TB, support is required through updated storage drivers. Storage driver support can be provided with - HP Pro 3500 | GPT Hard Disk Drives for HP Business Desktops - Page 7
utility will need to be manually selected to install in MBR format instead. To install in MBR mode, the user will need to access the boot menu using F9, then select "Legacy Boot Sources/ATAPI DVD Drive/SATA0" as shown in Figure 5. Figure 5. BIOs menu of HP UEFI BIOS system Drive Encryption For Opal - HP Pro 3500 | GPT Hard Disk Drives for HP Business Desktops - Page 8
at the following websites: For the UEFI specification, go to the UEFI SIG website at: http://www.uefi.org/home/ © 2011 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P. The information contained herein is subject to change without notice. The only warranties for HP products and services are set forth in the

GPT hard Disk Drives
For HP Desktops
April 2011
Table of Contents:
Abstract
..............................................................................................................
1
Why GPT?
...........................................................................................................
1
GPT vs MBR
........................................................................................................
2
Bootable vs Data Drives and UEFI BIOS
................................................................
4
OS Support
.........................................................................................................
6
Storage Driver Support
........................................................................................
6
Imaging Tool Support for GPT
..............................................................................
7
Drive Encryption
..................................................................................................
7
Summary
............................................................................................................
8
For more information
..........................................................................................
8
Abstract
In order to be used in a computer system, a hard disk drive (HDD) must first be
partitioned. Partitioning is done at the drive level and for many decades used the
Master Boot Record (MBR) partition method. A new method called GUID Partition
Table (GPT)) is now used for large-capacity drives. GPT allows for volume sizes
much greater than 2.19TB, and therefore must be used on drives larger than the
MBR limit of 2.19TB. This white paper describes the rationale for GPT and the types
of OS, BIOS, driver, and SW tool support needed to successfully implement GPT
drives in desktop systems.
Why GPT?
HDD areal density (bits/sq in) and tracks per inch (TPI) continue to steadily
increase. For 2010, many typical desktop 3.5” hard drives have areal densities
and TPI that permit capacities up to 500GB per platter. In 2011, it is expected that
improvements in areal density and TPI will allow drive manufacturers to begin
shipping drives that have capacities of1TB/platter. At this density, drives of 2TB
and 3TB capacities become more easily producible and hence cheaper and more
widely available.