HP Xw8200 Software RAID in Linux Workstations
HP Xw8200 - Workstation - 1 GB RAM Manual
 |
UPC - 882780210455
View all HP Xw8200 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
HP Xw8200 manual content summary:
- HP Xw8200 | Software RAID in Linux Workstations - Page 1
Software RAID in Linux Workstations Mini-White Paper Introduction...3 RAID Basics ...3 RAID Overview ...3 Software RAID in Linux ...3 Performance and Bottlenecks ...4 RAID Levels ...4 RAID-Linear: Concatenating Disks...4 RAID-0: Striping ...4 RAID-1: Mirroring...5 RAID-2: Error Checking and - HP Xw8200 | Software RAID in Linux Workstations - Page 2
The Persistent Superblock ...15 Chunk Sizes ...15 Swap Space in a RAID Configuration 16 Boot Partitions in a Mirrored RAID Configuration 16 Software RAID and LVM ...19 - HP Xw8200 | Software RAID in Linux Workstations - Page 3
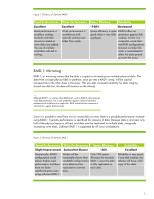
, recovery, and other information pertaining to running software RAID on a Linux system. Please note that while BIOS messages may refer to hardware RAID, hardware RAID is not supported by HP Linux workstations. RAID Basics RAID Overview Standing for Redundant Array of Independent (or Inexpensive - HP Xw8200 | Software RAID in Linux Workstations - Page 4
a hot-swap, however, the replacement for failed drives in software RAID requires only a minimum amount of work. Hardware RAID is not supported by HP Linux workstations. Performance and Bottlenecks Disk I/O bandwidth is typically limited by the system's bus speeds, the disk controller, and the disks - HP Xw8200 | Software RAID in Linux Workstations - Page 5
RAID-1, as well as other RAID levels such as RAID-5, does provide some data protection, this is only protection against common hardware problems such as failure of a single disk. RAID write times. Software RAID-1 is supported by HP Linux workstations. Figure 2. Efficiency of Software RAID-1 Read - HP Xw8200 | Software RAID in Linux Workstations - Page 6
parity disk, that disk can become a bottleneck. RAID-4 can work in some operations, but RAID-5 is generally preferred where a compromise between speed and reliability is sought. Software RAID-4 is not supported by HP Linux workstations. RAID-5: Block-Level Striping with Distributed Parity In order - HP Xw8200 | Software RAID in Linux Workstations - Page 7
when designing an ideal RAID workstation: Performance Multiple factors must be taken into account, including both random and sequential read and write speeds, latency times, and bus types; CPU and RAM configurations play a heavy part in the performance of a software RAID solution as well. Such - HP Xw8200 | Software RAID in Linux Workstations - Page 8
only allows for RAID-0, -1, and -5. The steps to configure software RAID using RHEL media are outlined below: 1. Power your HP workstation; boot to your RHEL installation media. 2. Continue through the installation until the "Disk Partitioning Setup" screen. 3. Select "Manually partition with Disk - HP Xw8200 | Software RAID in Linux Workstations - Page 9
Figure 4. Disk Partitioning Setup 4. Select "New" to create a new partition. 5. From the File System Type menu, choose "Software RAID." 6. Select one physical disk to create the partition on. 7. Choose the size of the partition. 8. Click OK. Figure 5. Disk Setup 9. Repeat steps 4-8 until all - HP Xw8200 | Software RAID in Linux Workstations - Page 10
installation. If you are creating a nested RAID array, you can either configure the "bottom" RAID level (for example, the RAID-1 array in the case of nested RAID-10) in Anaconda and the "top" RAID level manually later, or configure both parts of the nested RAID level manually after installation. 10 - HP Xw8200 | Software RAID in Linux Workstations - Page 11
put the /boot partition on a non-RAID part of the filesystem. Manual Setup of Software RAID Data Partitions While HP recommends using the above method to set up software RAID on your Linux workstations, it is possible to manually set up a software RAID partition on multiple disks after installation - HP Xw8200 | Software RAID in Linux Workstations - Page 12
Most of the work in manual configuration of a software RAID array comes from the creation of the appropriate /etc/raidtab file. The following are examples of /etc/raidtab files and the corresponding mdadm commands needed to set up each of the basic RAID configurations supported by HP. RAID-0 /etc - HP Xw8200 | Software RAID in Linux Workstations - Page 13
/etc/raidtab file: raiddev /dev/md0 raid-level nr-raid-disks nr-spare-disks chunk-size device raid-disk device raid-disk 0 2 0 4 /dev/sda1 0 /dev/sdb1 1 raiddev /dev/md1 raid-level nr-raid-disks nr-spare-disks chunk-size device raid-disk device raid-disk 0 2 0 4 /dev/sdc1 0 /dev/sdd1 1 raiddev - HP Xw8200 | Software RAID in Linux Workstations - Page 14
specific hard drive configuration. Disk Failure and Recovery Spare Disks and Disk Failure Spare disks are disks that do not take part in the RAID that is not failed. Removing and replacing a failed disk can be done as follows: 1. Remove the failed disk from the RAID array by running the command: - HP Xw8200 | Software RAID in Linux Workstations - Page 15
't work, you can run: mkraid --force to rewrite the RAID superblocks. In order for this to work, set of disks. If you had two disks and wanted to write a byte, you would have to write four bits on each disk, with every second bit going to disk 0 and the others to disk 1. Hardware doesn't support - HP Xw8200 | Software RAID in Linux Workstations - Page 16
physical hard disk that will be part of the RAID-1 array. This is easiest when done during the original installation and configuration of the Linux workstation. The steps to manually mirror your boot partition are outlined below: 1. Power your HP workstation; boot to your RHEL installation media - HP Xw8200 | Software RAID in Linux Workstations - Page 17
Figure 8. Disk Partitioning Setup 4. On each disk that will be in the RAID-1 array, create a partition that will be bootable. One drive should have the actual /boot partition; each other , and so on for each hard disk. 5. Create a bootable partition on each disk that will be in the RAID-1 array. 17 - HP Xw8200 | Software RAID in Linux Workstations - Page 18
workstation. You should now have a partition that will be made bootable on each hard disk in the RAID array. You can verify your current disk setup by running the df command in a terminal window mount it if you are running a kernel update. After the update is complete, repeat these steps to mirror - HP Xw8200 | Software RAID in Linux Workstations - Page 19
Setup of the filesystem can now continue as normal. © 2006 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P. The information contained herein is subject to change without notice. The only warranties for HP products and services are set forth in the express warranty statements accompanying such products and

Software RAID in Linux Workstations
Mini-White Paper
Introduction
.........................................................................................................................................
3
RAID Basics
........................................................................................................................................
3
RAID Overview
................................................................................................................................
3
Software RAID in Linux
.....................................................................................................................
3
Performance and Bottlenecks
.............................................................................................................
4
RAID Levels
.........................................................................................................................................
4
RAID-Linear: Concatenating Disks
.......................................................................................................
4
RAID-0: Striping
...............................................................................................................................
4
RAID-1: Mirroring
.............................................................................................................................
5
RAID-2: Error Checking and Correction
..............................................................................................
6
RAID-3: Byte-Level Striping with Parity Disk
..........................................................................................
6
RAID-4: Block-Level Striping with Parity Disk
........................................................................................
6
RAID-5: Block-Level Striping with Distributed Parity
...............................................................................
6
Additional RAID Levels
......................................................................................................................
7
RAID Configuration Strategies
...............................................................................................................
7
Performance
....................................................................................................................................
7
Capacity versus Fault-Tolerance
.........................................................................................................
7
Cost
...............................................................................................................................................
7
RAID Performance Considerations
......................................................................................................
8
Configuring Red Hat Enterprise Linux with Software RAID
.........................................................................
8
Manual Setup of Software RAID Data Partitions
.....................................................................................
11
Manual Configuration Examples
..........................................................................................................
12
RAID-0
..........................................................................................................................................
12
RAID-1
..........................................................................................................................................
12
RAID-5
..........................................................................................................................................
13
RAID-10
........................................................................................................................................
13
Disk Failure and Recovery
...................................................................................................................
14
Spare Disks and Disk Failure
...........................................................................................................
14
Multiple Disk Failure
.......................................................................................................................
15
Additional Configuration Information
...................................................................................................
15