Honeywell HPFF12 Operation Manual - Page 49
Calculating the System Current Draw, 6.3.1 Overview, Overview
 |
View all Honeywell HPFF12 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 49 highlights
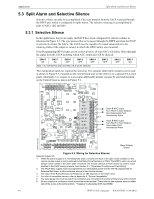
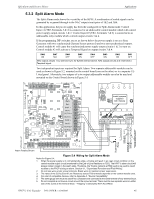
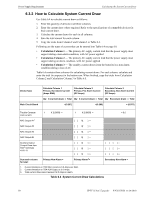
Calculating the System Current Draw Power Supply Requirements 6.3 Calculating the System Current Draw 6.3.1 Overview The power supply must be able to power all internal and external devices continuously during the non-alarm condition. To calculate the non-alarm condition load on the power supply when primary power is applied, use the Calculation Column 1 in Table 6.4. The power supply must support a larger load current during an alarm condition. To calculate the fire alarm load on the power supply, use the Calculation Column 2 in Table 6.4. The secondary power source (batteries) must be able to power the system during primary power loss. To calculate the non-alarm condition load on the power supply when primary power is applied, use the Calculation Column 3 in Table 6.4. When calculating current draw and the battery size, note the following: • Primary refers to the main AC power source for the power supply. • Secondary refers to the Power supply's backup batteries. • All currents are given in amperes (A). Table 6.2 shows how to convert milliamperes and microamperes to full amperes. To convert... Multiply Example Milliamperes (mA) to amperes (A) mA x 0.001 3 mA x 0.001 = 0.003 A Microamperes (µA) to amperes (A) µA x 0.000001 300 µA x 0.000001 = 0.0003 A Table 6.2 Converting to Full Amperes The following table shows the maximum number of Notification Appliances that can be connected to the NAC outputs per manufacturer. These maximum numbers are equivalent to the full 12 Amps capability of the power supply. The maximum number of devices will have to be reduced if an Auxiliary load is present, see Table 6.4. Device Manufacturer Maximum Number of Devices Cooper Wheelock 200 total 50 for 3.0 Amp loaded NAC System Sensor SpectrAlert Advanced 184 total 46 for 3.0 Amp loaded NAC SpectrAlert 200 total 50 for 3.0 Amp loaded NAC Amseco 136 total 34 for 3.0 Amp loaded NAC Faraday 132 total 33 for 3.0 Amp loaded NAC Gentex 144 total 36 for 3.0 Amp loaded NAC Table 6.3 Maximum Number of Notification Appliances per Extender HPFF12 NAC Expander - P/N 53576:B 11/24/2010 49