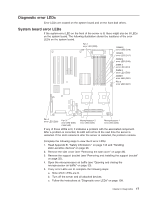
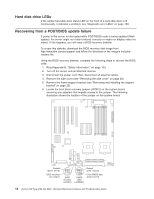
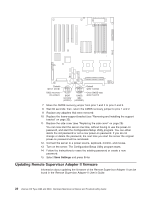
IBM 84885BU User Manual - Page 31
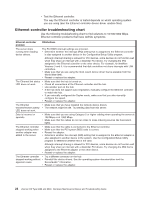
Power, checkout, Troubleshooting, Ethernet, controller, Network, connection, problems
 |
View all IBM 84885BU manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 31 highlights
Power checkout Power problems can be difficult to solve. For example, a short circuit can exist anywhere on any of the power distribution buses. Usually a short circuit will cause the power subsystem to shut down because of an overcurrent condition. Follow this general procedure for troubleshooting power problems: 1. Turn off the server and disconnect all ac power cords. 2. Check for loose cables in the power subsystem. Also check for short circuits. For example, a loose screw can cause a short circuit on a circuit board. 3. Remove adapters and disconnect the cables and power connectors to all internal and external devices until the server is at the minimum configuration that is required to start the server (see "Minimum operating requirements" on page 117). 4. Reconnect all ac power cords and turn on the server. If the server starts up successfully, replace adapters and devices one at a time until the problem is isolated. If the server does not start up from the minimal configuration, replace FRUs of minimal configuration one at a time until the problem is isolated. To use this method, you must know the minimum configuration that is required for the server to start (see page 127). Troubleshooting the Ethernet controller This section provides troubleshooting information for problems that might occur with the 10/100/1000 Mbps Ethernet controller. Network connection problems If the Ethernet controller cannot connect to the network, check the following conditions: v Make sure that the cable is installed correctly. The network cable must be securely attached at all connections. If the cable is attached but the problem remains, try a different cable. If you set the Ethernet controller to operate at either 100 Mbps or 1000 Mbps, you must use Category 5 or higher cabling. v Determine whether the hub supports auto-negotiation. If it does not, try configuring the integrated Ethernet controller manually to match the speed and duplex mode of the hub. v Check the Ethernet controller LEDs on the rear of the server. These LEDs indicate whether there is a problem with the connector, cable, or hub: - The Ethernet transmit/receive activity LED, on the rear of the server, is lit when the Ethernet controller sends or receives data over the Ethernet Network. If the Ethernet transmit/receive activity LED is off, make sure that the hub and network are operating and that the correct device drivers are installed. - The Ethernet link status LED, on the rear of the server, is lit when the Ethernet controller receives a LINK pulse from the hub. If the LED is off, there might be a defective connector or cable or a problem with the hub. v Make sure that you are using the correct device drivers, which are supplied with the server. v Check for operating-system-specific causes for the problem. v Make sure that the device drivers on the client and server are using the same protocol. Chapter 3. Diagnostics 21