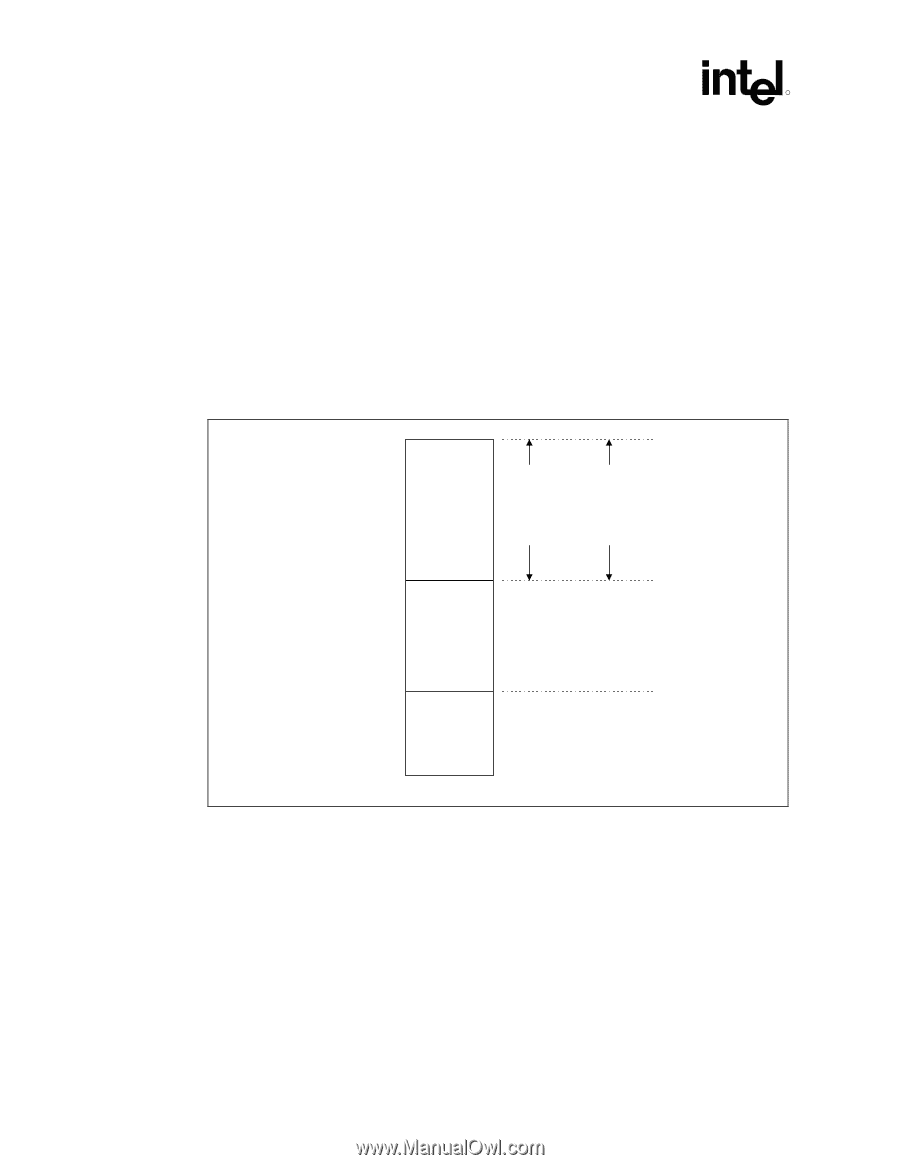Intel 925 Data Sheet - Page 158
Legacy Address Range, System Address Ranges
 |
UPC - 683728067724
View all Intel 925 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 158 highlights
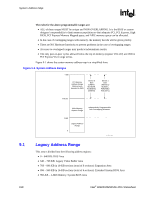
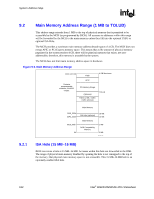
System Address Map R The rules for the above programmable ranges are: • ALL of these ranges MUST be unique and NON-OVERLAPPING. It is the BIOS or system designer's responsibility to limit memory population so that adequate PCI, PCI Express, High BIOS, PCI Express Memory Mapped space, and APIC memory space can be allocated. • In the case of overlapping ranges with memory, the memory decode will be given priority. • There are NO Hardware Interlocks to prevent problems in the case of overlapping ranges. • Accesses to overlapped ranges may produce indeterminate results. • The only peer-to-peer cycles allowed below the top of memory (register TOLUD) are DMI to PCI Express VGA range writes. Figure 9-1 shows the system memory address map in a simplified form. Figure 9-1. System Address Ranges 4 GB PCI Memory Address Range (Subtractively decoded to DMI) Device 0 Bars (EPBAR, MCHBAR, PCIEXBAR, DMIBAR) Device 1 Bars (MBASE1/ MLIMIT1, PMBASE1/ PMLIMIT1) TOLUD Main Memory Address Range Independently Programmable Non-Overlapping Windows 1 MB Legacy Address Range 0 Sys_Address_Ranges 9.1 Legacy Address Range This area is divided into the following address regions: • 0 - 640 KB: DOS Area • 640 - 768 KB: Legacy Video Buffer Area • 768 - 896 KB in 16-KB sections (total of 8 sections): Expansion Area • 896 - 960 KB in 16-KB sections (total of 4 sections): Extended System BIOS Area • 960-KB - 1-MB Memory: System BIOS Area 158 Intel® 82925X/82925XE MCH Datasheet