Intel 925 Data Sheet - Page 161
Extended System BIOS Area E_0000h-E_FFFFh, Programmable Attribute Map PAM Memory Area Details
 |
UPC - 683728067724
View all Intel 925 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 161 highlights
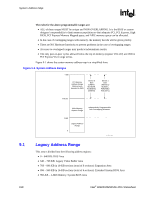
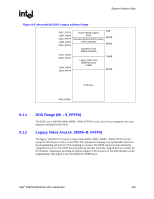
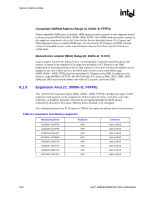
System Address Map R 9.1.4 Extended System BIOS Area (E_0000h-E_FFFFh) This 64-KB area (000E_0000h-000E_FFFFh) is divided into four, 16-KB segments. Each segment can be assigned independent read and write attributes so it can be mapped either to main DRAM or to the DMI. Typically, this area is used for RAM or ROM. Memory segments that are disabled are not remapped elsewhere. Non-snooped accesses from PCI Express or DMI to this region are always sent to main memory. Table 9-2. Extended System BIOS Area Memory Segments Memory Segments 0E0000h-0E3FFFh 0E4000h-0E7FFFh 0E8000h-0EBFFFh 0EC000h-0EFFFFh Attributes W/R W/R W/R W/R Comments BIOS Extension BIOS Extension BIOS Extension BIOS Extension 9.1.5 System BIOS Area (F_0000h-F_FFFFh) This area is a single, 64-KB segment (000F_0000h - 000F_FFFFh). This segment can be assigned read and write attributes. It is by default (after reset) read/write disabled and cycles are forwarded to the DMI. By programming the read/write attributes, the MCH can "shadow" BIOS into main memory. When disabled, this segment is not remapped. Non-snooped accesses from PCI Express or DMI to this region are always sent to main memory. Table 9-3. System BIOS Area Memory Segments Memory Segments 0F0000h-0FFFFFh Attributes WE RE Comments BIOS Area 9.1.6 Programmable Attribute Map (PAM) Memory Area Details The 13 sections from 768 KB to 1 MB comprise what is also known as the PAM memory area. The MCH does not handle IWB (Implicit Write-Back) cycles targeting DMI. Since all memory residing on DMI should be set as non-cacheable, there will normally not be IWB cycles targeting DMI. However, DMI becomes the default target for processor and DMI originated accesses to disabled segments of the PAM region. If the MTRRs covering the PAM regions are set to WB or RC, it is possible to get IWB cycles targeting DMI. This may occur for DMI-originated cycles to disabled PAM regions. Note: For example, assume that a particular PAM region is set for "Read Disabled" and the MTRR associated with this region is set to WB. A DMI master generates a memory read targeting the PAM region. A snoop is generated on the FSB and the result is an IWB. Since the PAM region is "Read Disabled", the default target for the memory read becomes DMI. The IWB associated with this cycle will cause the MCH to hang. Intel® 82925X/82925XE MCH Datasheet 161