Intel 925 Data Sheet - Page 18
Direct Media Interface DMI, PCI Express* Graphics Interface
 |
UPC - 683728067724
View all Intel 925 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 18 highlights
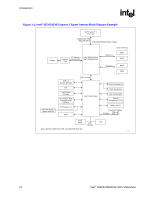
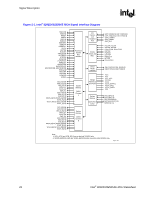
Introduction R 1.3.3 1.3.4 Direct Media Interface (DMI) Direct Media Interface (DMI) is the chip-to-chip connection between the MCH and ICH6. This high-speed interface integrates advanced priority-based servicing allowing for concurrent traffic and true isochronous transfer capabilities. Base functionality is completely software transparent permitting current and legacy software to operate normally. To provide for true isochronous transfers and configurable Quality of Service (QoS) transactions, the ICH6 supports two virtual channels on DMI: VC0 and VC1. These two channels provide a fixed arbitration scheme where VC1 is always the highest priority. VC0 is the default conduit of traffic for DMI and is always enabled. VC1 must be specifically enabled and configured at both ends of the DMI link (i.e., the ICH6 and MCH). Features of the DMI include: • A chip-to-chip connection interface to ICH6 • 2 GB/s point-to-point DMI to ICH6 (1 GB/s each direction) • 100 MHz reference clock (shared with PCI Express Graphics Attach). • 32-bit downstream addressing • APIC and MSI interrupt messaging support. Will send Intel-defined "End Of Interrupt" broadcast message when initiated by the processor. • Message Signaled Interrupt (MSI) messages • SMI, SCI and SERR error indication • Legacy support for ISA regime protocol (PHOLD/PHOLDA) required for parallel port DMA, floppy drive, and LPC bus masters PCI Express* Graphics Interface The MCH contains a 16-lane (x16) PCI Express* port intended for an external PCI Express graphics card. The PCI Express port is compatible with the PCI Express Base Specification Revision 1.0a. The x16 port operates at a frequency of 2.5 Gb/s on each lane while employing 8b/10b encoding, and supports a maximum theoretical bandwidth of 4 Gb/s each direction. 18 Intel® 82925X/82925XE MCH Datasheet