Intel BLKDX58OG Product Specification - Page 22
Real-Time Clock Subsystem, Legacy I/O Controller
 |
View all Intel BLKDX58OG manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 22 highlights
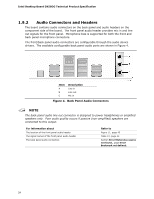
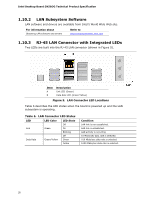
Intel Desktop Board DX58OG Technical Product Specification 1.7 Real-Time Clock Subsystem A coin-cell battery (CR2032) powers the real-time clock and CMOS memory. When the computer is not plugged into a wall socket, the battery has an estimated life of three years. When the computer is plugged in, the standby current from the power supply extends the life of the battery. The clock is accurate to ± 13 minutes/year at 25 ºC with 3.3 VSB applied. NOTE If the battery and AC power fail, Date and Time values will be reset and the user will be notified during POST. When the voltage drops below a certain level, the BIOS Setup program settings stored in CMOS RAM (for example, the date and time) might not be accurate. Replace the battery with an equivalent one. Figure 1 on page 13 shows the location of the battery. 1.8 Legacy I/O Controller The I/O controller provides the following features: • Consumer Infrared (CIR) headers • Serial IRQ interface compatible with serialized IRQ support for PCI systems • Intelligent power management, including a programmable wake-up event interface • PCI power management support The BIOS Setup program provides configuration options for the I/O controller. 1.8.1 Consumer Infrared (CIR) The Consumer Infrared (CIR) feature is designed to comply with Microsoft Consumer Infrared usage models. Microsoft Windows Vista is the supported operating system The CIR feature is made up of two separate pieces: the receiving (receiver) header, and the output (emitter) header. The receiving header consists of a filtered translated infrared input compliant with Microsoft CIR specifications, and also a "learning" infrared input. This learning input is simply a high pass input which the computer can use to "learn" to speak the infrared communication language of other user remotes. The emitter header consists of two output ports which the PC can use to emulate "learned" infrared commands in order to control external electronic hardware. Customers are required to buy or create their own interface modules to plug into Intel Desktop Boards for this feature to work. 22