Kyocera KM-8030 PRESCRIBE Commands Technical Reference Manual - Rev. 4.7 - Page 47
Printout of the PARC Example, R! RES UNIT C; NEWP; SPD .1, PMRA 5
 |
View all Kyocera KM-8030 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 47 highlights
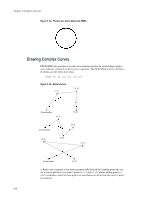
Figure 2. 22. Printout of the PARC Example Path Mode Graphics After the arc is drawn, the cursor is located at the end of the arc. If you wish to eliminate the straight line segment in the above example, leaving only the arc, the cursor position must be moved in advance to the position at which drawing of the arc begins. This is shown in the following example, in which the cursor is moved to the coordinates as specified by the PMRA (Path, Move to Relative position specified by Angle) command prior to drawing the arc. !R! RES UNIT C; NEWP; SPD .1; PMRA 5, 5, 3, 45; PARC 5, 5, 3, 45, 135; STRK; PAGE; EXIT; In this current example, the PMRA command moves the cursor from coordinates 5, 5, as measured from the left and top edge limits of the page, through the distance of 3 centimeters at the angle of 45 degrees from the positive x axis. At this point, the PARC command starts to draw the arc which ends at the angle of 135 degrees. Figure 2. 23. Printout of the PMRA Example Circles can be constructed by drawing arcs with angular extents of 360 degrees. To draw a circle, you will also need a PMRA command to eliminate the line extending from the center of the circle to the beginning of the circle. See the following example: !R! RES; UNIT C; NEWP; SPD .1; PMRA 3, 3, 1.5, 0; PARC 3, 3, 1.5, 0, 360; STRK; PAGE; EXIT; 2-25