Lexmark C534n User's Guide - Page 98
Menus and Messages Guide, Software, and Documentation, Software and Documentation, User's Guide - color laser printer
 |
UPC - 734646258524
View all Lexmark C534n manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 98 highlights
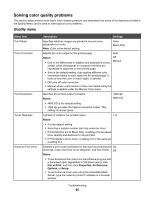
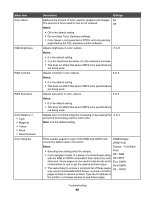
What is CMYK color? Cyan, magenta, yellow, and black inks or toners can be printed in various amounts to produce a large range of colors observed in nature. For example, cyan and yellow can be combined to create green. Printing presses, inkjet printers, and color laser printers create colors in this manner. CMYK color is a method of describing colors by indicating the amount of cyan, magenta, yellow, and black needed to reproduce a particular color. How is color specified in a document to be printed? Software programs typically specify document color using RGB or CMYK color combinations. Additionally, they commonly let users modify the color of each object in a document. For more information, see the software program Help section. How does the printer know what color to print? When a user prints a document, information describing the type and color of each object is sent to the printer. The color information is passed through color conversion tables that translate the color into appropriate amounts of cyan, magenta, yellow, and black toner needed to produce the desired color. The object type information lets different color conversion tables be used for different types of objects. For example, it is possible to apply one type of color conversion table to text while applying a different color conversion table to photographic images. Should I use PostScript or PCL emulation printer software? What settings should I use for the best color? The PostScript driver is strongly recommended for best color quality. The default settings in the PostScript driver provide preferred color quality for the majority of printouts. Why doesn't the printed color match the color I see on the computer screen? The color conversion tables used in Auto Color Correction mode generally approximate the colors of a standard computer monitor. However, because of technology differences that exist between printers and monitors, there are many colors that can also be affected by monitor variations and lighting conditions. For recommendations on how the printer color sample pages may be useful in solving certain color-matching problems, see the question, "How can I match a particular color (such as a color in a corporate logo)?" The printed page appears tinted. Can I slightly adjust the color? Sometimes a user may consider printed pages to appear tinted (for example, everything printed seems to be too red). This can be caused by environmental conditions, paper type, lighting conditions, or user preference. In these instances, adjusting the Color Balance setting may be used to create more preferable color. Color Balance provides the user with the ability to make subtle adjustments to the amount of toner being used in each color plane. Selecting positive (or negative) values for cyan, magenta, yellow, and black under the Color Balance menu will slightly increase (or decrease) the amount of toner used for the chosen color. For example, if a user believes the overall printed page to be too red, then decreasing both magenta and yellow could potentially improve color preferences. For information about adjusting the Color Balance setting, see the Menus and Messages Guide on the Software and Documentation CD. My color transparencies seem dark when being projected. Is there anything I can do to improve the color? This problem most commonly occurs when projecting transparencies with reflective overhead projectors. To obtain the highest projected color quality, transmissive overhead projectors are recommended. If a reflective projector must be used, then adjusting the Toner Darkness setting to 1, 2, or 3 will lighten the transparency. For more information, see the Menus and Messages Guide on the Software and Documentation CD. Make sure to print on the recommended type of color transparencies. For more information about the paper and media specifications, see the User's Guide on the Software and Documentation CD. What is manual color correction? The color conversion tables applied to each object when using the default Auto Color Correction setting generate preferred color for the majority of documents. Occasionally, a user may want to apply a different color table mapping. This customization is accomplished using the Manual Color menu and the Manual Color Correction setting. Troubleshooting 98