Lexmark X5650 Network Guide - Page 25
What is a network?
 |
UPC - 734646078566
View all Lexmark X5650 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 25 highlights
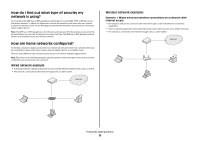
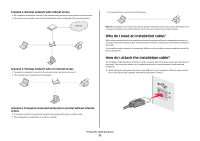
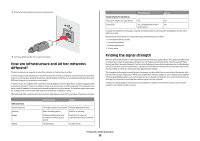
Frequently asked questions Where do I find my WEP key or WPA passphrase? To find the WEP key or WPA passphrase for the wireless network, view the security settings on the access point or wireless router. Most access points have a built-in Web server that can be accessed using a Web browser. If you do not know how to access the built-in Web server, or if you do not have administrator access to the wireless access point on your network, contact your system support person. What is an SSID? A Service Set Identifier (SSID) is the name that identifies a wireless network. All devices on the network must know the SSID of the wireless network or they will not be able to communicate with each other. Usually, the wireless network broadcasts the SSID to allow wireless devices in the area to connect to it. Sometimes, the SSID is not broadcast for security reasons. If the SSID of your wireless network is not broadcast, it cannot be detected automatically and will not show up in the list of available wireless networks. You must enter the network information manually in this situation. An SSID can contain up to 32 alphanumeric characters. Where do I find my SSID? You can find the SSID for the wireless network by viewing the settings on the access point or wireless router. Most access points have a built-in Web server that can be accessed using a Web browser. Many network adapters provide a software application that allows you to view the wireless settings of your computer, including your SSID. Check your computer to see if a program was installed with your network adapter. If you are unable to locate your SSID using either of these methods, contact your system support person. What is a network? A network is a collection of devices such as computers, printers, Ethernet hubs, wireless access points, and routers connected together for communication through cables or through a wireless connection. A network can be wired, wireless, or designed to have both wired and wireless devices. Devices on a wired network use cables to communicate with each other. Devices on a wireless network use radio waves instead of cables to communicate with each other. For a device to be able to communicate wirelessly, it must have a wireless print server attached or installed that lets it receive and transmit radio waves. What types of wireless network security are available? The wireless printer supports four security options: no security, WEP, WPA, and WPA2. No Security It is not recommended to use no security at all on a home wireless network. Using no security means that anyone within range of your wireless network can use your network resources-including Internet access, if your wireless network is connected to the Internet. The range of your wireless network may extend far beyond the walls of your home, allowing access to your network from the street or from your neighbors' homes. Ad hoc networks, which do not use wireless access points or routers, may be safely used without security. The range of an ad hoc network is very short, making unauthorized access unlikely. WEP WEP (Wireless Equivalent Privacy) is the most basic and the weakest type of wireless security. WEP security relies on a series of characters called the WEP key. Every device on the wireless network must use the same WEP key. WEP security can be used on both ad hoc and infrastructure networks. A valid WEP key has: • Exactly 10 or 26 hexadecimal characters. Hexadecimal characters are A-F, a-f, and 0-9 or • Exactly 5 or 13 ASCII characters. ASCII characters are letters, numbers, punctuation, and symbols found on a keyboard. WPA and WPA2 WPA (Wi-Fi Protected Access) and WPA2 (Wi-Fi Protected Access 2) offer stronger wireless network security than WEP. WPA and WPA2 are similar types of security. WPA2 is a newer version of WPA and is more secure than WPA. Both WPA and WPA2 use a series of characters, called the WPA pre-shared key or passphrase, to protect wireless networks from unauthorized access. A valid WPA passphrase has: • From 8 to 63 ASCII characters. ASCII characters in a WPA passphrase are case-sensitive. or • Exactly 64 hexadecimal characters. Hexadecimal characters are A-F, a-f, and 0-9. Every device on the wireless network must use the same WPA passphrase. WPA security is an option only on infrastructure networks with wireless access points and network cards that support WPA. Most newer wireless network equipment also offers WPA2 security as an option. Frequently asked questions 25