Netgear DGN2200 DGN2200 User Manual - Page 100
Port Forwarding and Port Triggering, Port Forwarding
 |
UPC - 606449067279
View all Netgear DGN2200 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 100 highlights
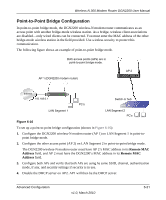
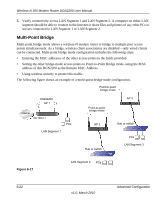
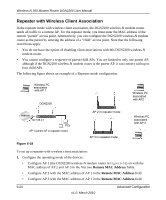
Wireless-N 300 Modem Router DGN2200 User Manual 2. Verify the following for both access points: • The LAN network configuration of each AP is configured to operate in the same LAN network address range as the LAN devices. • The APs must be on the same LAN. That is, the LAN IP addresses for the APs must be in the same network. • If you are using DHCP, AP devices should be set to Obtain an IP address automatically (DHCP Client) in the IP Address Source section of the Basic IP Settings screen. • AP devices must use the same SSID, channel, authentication mode, and encryption. 3. Verify connectivity across the LANs. A computer on any LAN segment should be able to connect to the Internet or share files and printers with any other PCs or servers connected to any of the three WLAN segments. Port Forwarding and Port Triggering Port forwarding and port triggering are advanced features that affect the behavior of the firewall in your wireless-N modem router. Using the Port Forwarding / Port Triggering screen, you can make local computers or servers available to the Internet for different services (for example, FTP or HTTP), to play Internet games (like Quake III), or to use Internet applications (like CU-SeeMe) • Port triggering Port triggering monitors outbound traffic. When the router detects traffic on the specified outbound port, it remembers the IP address of the computer that sent the data and triggers the incoming port. Incoming traffic on the triggered port is then forwarded to the triggering computer. Port triggering allows requests from the Internet only after a designated port is triggered. Port triggering applies to chat and Internet games. • Port forwarding is designed for FTP, Web server, or other server-based services. Once port forwarding is set up, requests from the Internet are forwarded to the proper server. Port Forwarding To set up port forwarding: 1. From the main menu, under the Advanced Heading, select Port Forwarding/Port Triggering. The following screen displays: Advanced Configuration v1.0, March 2010 6-25