Netgear DGN2200 DGN2200 User Manual - Page 98
Remote MAC Address 1, Obtain an IP address, automatically DHCP Client
 |
UPC - 606449067279
View all Netgear DGN2200 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 98 highlights
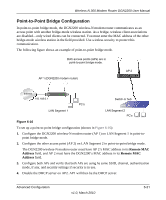
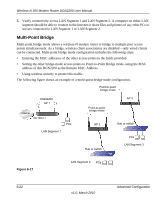
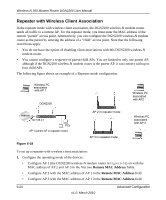
Wireless-N 300 Modem Router DGN2200 User Manual To set up the multi-point bridge configuration shown in Figure 6-17: 1. Configure the operating mode of the wireless-N modem routers. • Because it is in a central location, configure the DGN2200 wireless-N modem router (AP 1) on LAN Segment 1 in point-to-multi-point bridge mode, and enter the MAC addresses of AP-2 and AP-3 in the Remote MAC Address 1 and Remote MAC Address 2 fields. • Configure the access point (AP2) on LAN Segment 2 in point-to-point bridge mode with the remote MAC address of the DGN2200 wireless-N modem router. • Configure the access point (AP3) on LAN Segment 3 in point-to-point bridge mode with the remote MAC address of the DGN2200 wireless-N modem router. 2. Disable the DHCP server on AP2 and AP3. AP1 will then be the DHCP server. 3. Verify the following for all access points: • The LAN network configuration of the wireless-N modem router and other access points are configured to operate in the same LAN network address range as the LAN devices. • Only one AP, the DGN2200 wireless-N modem router in Figure 6-17, is configured in point-to-multi-point bridge mode; all the others are in point-to-point bridge mode. • All APs, including the DGN2200 wireless-N modem router, must be on the same LAN. That is, all the AP LAN IP addresses must be in the same network. • If you are using DHCP, all access points should be set to Obtain an IP address automatically (DHCP Client) in the IP Address Source section of the Basic IP Settings screen. • All APs, including the DGN2200 wireless-N modem router, must use the same SSID, channel, authentication mode, if any, and WEP security settings if security is in use. • All point-to-point APs must have the MAC address of AP 1 (the DGN2200 wireless-N modem router in the previous figure) in the Remote AP MAC address field. 4. Verify connectivity across the LANs. • A computer on any LAN segment should be able to connect to the Internet or share files and printers with any other PCs or servers connected to any of the three LAN segments. Note: Wireless stations configured as they are in Figure 6-17 will not be able to connect to the wireless-N modem router or access points. If you require wireless stations to access any LAN segment, you can use additional access points configured in wireless access point mode in any LAN segment. Advanced Configuration v1.0, March 2010 6-23