Netgear DGN2200v3 DGN2200v3 User Manual - Page 93
Wireless Bridging and Repeating Networks, Wireless Settings Screen, Set Up a Point-to-Point Bridge
 |
View all Netgear DGN2200v3 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 93 highlights
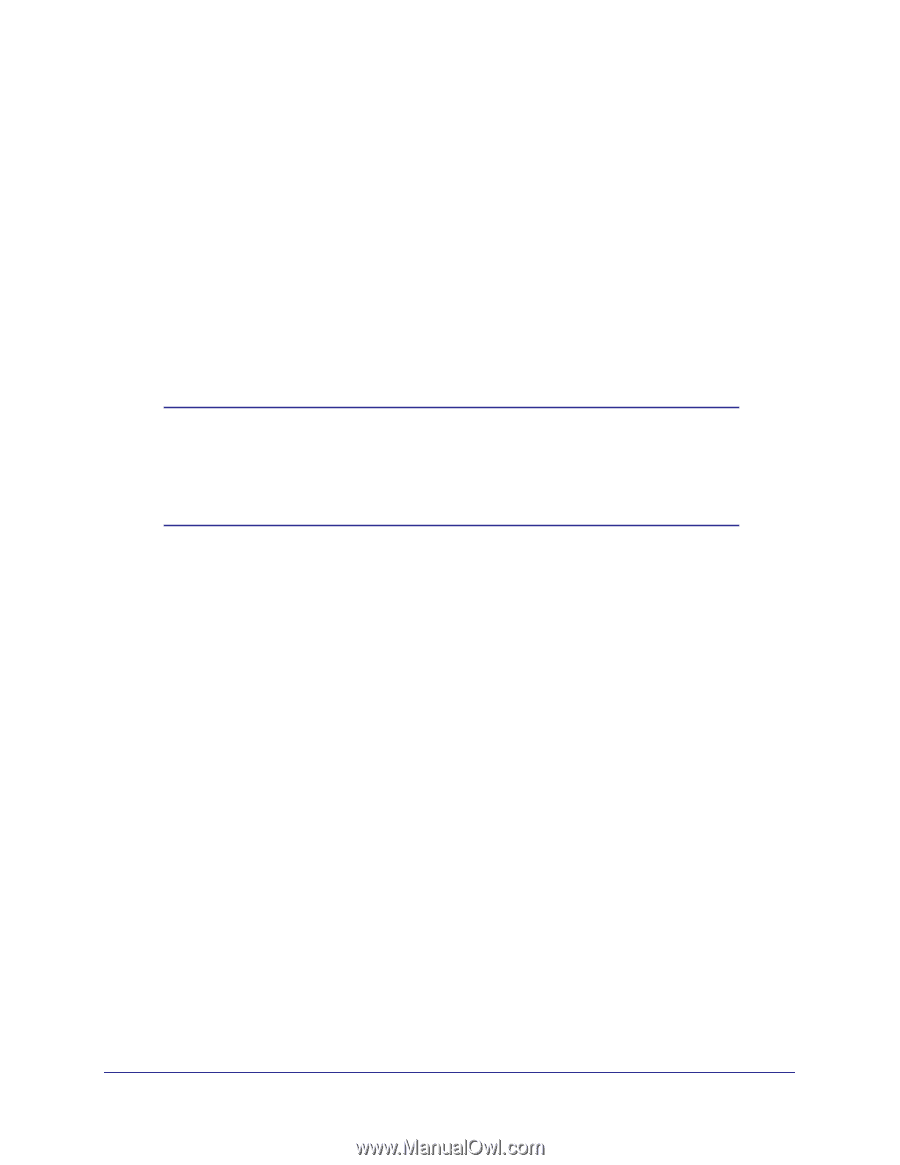
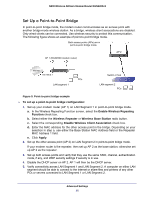
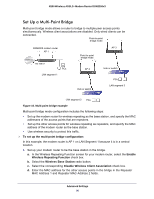
N300 Wireless ADSL2+ Modem Router DGN2200v3 5. Set the Traffic Counter to begin at a specific time and date. 6. Set up Traffic Control to issue a warning message before the monthly limit of Mbytes or hours is reached. You can select one of the following to occur when the limit is attained: • The Internet LED flashes green or amber. • The Internet connection is disconnected and disabled. 7. Set up Internet Traffic Statistics to monitor the data traffic. 8. Click the Traffic Status button if you want a live update on Internet traffic status on your modem router. 9. Click Apply to save your settings. Wireless Bridging and Repeating Networks Note: If you want to use the Wireless Repeating feature, you have to go to the Wireless Settings screen and change the wireless security setting of the router to WEP or None, and you have to change the Channel field to a different setting than Auto, which is the default. For more information, see Wireless Settings Screen on page 33. With the modem router, you can build large bridged wireless networks that form an IEEE 802.11n Wireless Distribution System (WDS). Using the modem router with other access points (APs) and wireless devices, you can connect clients using their MAC addresses rather than IP addresses. Here are some examples of wireless bridged configurations: • Point-to-point bridge. The modem router communicates with another bridge-mode wireless station. See Set Up a Point-to-Point Bridge on page 95. • Multi-point bridge. The modem router is the "master" for a group of bridge-mode wireless stations. Then all traffic is sent to this master, rather than to other access points. See Set Up a Multi-Point Bridge on page 96. • Repeater with wireless client association. Sends all traffic to the remote access point. See Repeater with Wireless Client Association on page 97. The wireless bridging and repeating feature uses the default security profile to send and receive traffic. Advanced Settings 93