Netgear WNR1000v2 WNR1000v2 User Manual - Page 60
Configuring a Device Name, Configuring LAN TCP/IP Setup Parameters, Device Name - default ip
 |
View all Netgear WNR1000v2 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 60 highlights
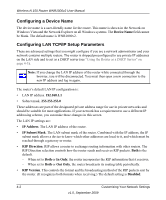
Wireless-N 150 Router WNR1000v2 User Manual Configuring a Device Name The device name is a user-friendly name for the router. This name is shown in the Network on Windows Vista and the Network Explorer on all Windows systems. The Device Name field cannot be blank. The default name is WNR1000v2. Configuring LAN TCP/IP Setup Parameters These are advanced settings that you might configure if you are a network administrator and your network contains multiple routers. The router is shipped preconfigured to use private IP addresses on the LAN side and to act as a DHCP server (see "Using the Router as a DHCP Server" on page 4-3). Note: If you change the LAN IP address of the router while connected through the browser, you will be disconnected. You must then open a new connection to the new IP address and log in again. The router's default LAN IP configuration is: • LAN IP address. 192.168.1.1 • Subnet mask. 255.255.255.0 These addresses are part of the designated private address range for use in private networks and should be suitable for most applications. If your network has a requirement to use a different IP addressing scheme, you can make those changes in this screen. The LAN IP settings are: • IP Address. The LAN IP address of the router. • IP Subnet Mask. The LAN subnet mask of the router. Combined with the IP address, the IP subnet mask allows a device to know which other addresses are local to it, and which must be reached through a gateway or router. • RIP Direction. RIP allows a router to exchange routing information with other routers. The RIP Direction selection controls how the router sends and receives RIP packets. Both is the default. - When set to Both or In Only, the router incorporates the RIP information that it receives. - When set to Both or Out Only, the router broadcasts its routing table periodically. • RIP Version. This controls the format and the broadcasting method of the RIP packets sent by the router. (It recognizes both formats when receiving.) The default setting is Disabled. 4-2 Customizing Your Network Settings v1.0, September 2009