Netgear WNR1000v2 WNR1000v2 User Manual - Page 84
Overview of Home and Small Office Networking Technologies, WAN Setup, MTU Size, Apply
 |
View all Netgear WNR1000v2 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 84 highlights
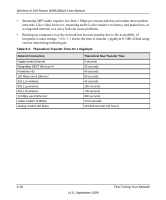
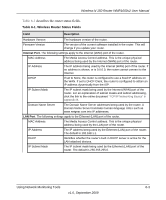
Wireless-N 150 Router WNR1000v2 User Manual If you suspect an MTU problem, a common solution is to change the MTU size to 1400. If you are willing to experiment, you can gradually reduce the MTU size from the maximum value of 1500 until the problem goes away. Table 5-1 describes common MTU sizes and applications. Table 5-1. Common MTU Sizes MTU 1500 1492 1472 1468 1460 1436 1400 576 Application The largest Ethernet packet size and the default value. This is the typical setting for nonPPPoE, non-VPN connections, and is the default value for NETGEAR routers, adapters, and switches. Used in PPPoE environments. Maximum size to use for pinging. (Larger packets are fragmented.) Used in some DHCP environments. Usable by AOL if you do not have large e-mail attachments, for example. Used in PPTP environments or with VPN. Maximum size for AOL DSL. Typical value to connect to dial-up ISPs. To change the MTU size: 1. In the main menu, under Advanced, select WAN Setup. 2. In the MTU Size field, enter a new size between 64 and 1500. 3. Click Apply to save the new configuration. Overview of Home and Small Office Networking Technologies Common connection types and their speed and security considerations are: • Broadband Internet. Your Internet connection speed is determined by your modem type, such as ADSL or cable modem, as well as the connection speed of the sites to which you connect, and general Internet traffic. ADSL and cable modem connections are asymmetrical, meaning they have a lower data rate to the Internet (upstream) than from the Internet (downstream). Keep in mind that when you connect to another site that also has an asymmetrical connection, the data rate between your sites is limited by each side's upstream data rate. A typical residential ADSL or cable modem connection provides a downstream throughput of about 1 to 3 megabits per second (Mbps). Newer technologies such as ADSL2+ and Fiber to the Home (FTTH) will increase the connection speed to tens of Mbps. 5-16 v1.0, September 2009 Fine-Tuning Your Network