TP-Link TL-WA5110G User Guide - Page 46
Wireless settings, Forwarding
 |
UPC - 845973051327
View all TP-Link TL-WA5110G manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 46 highlights
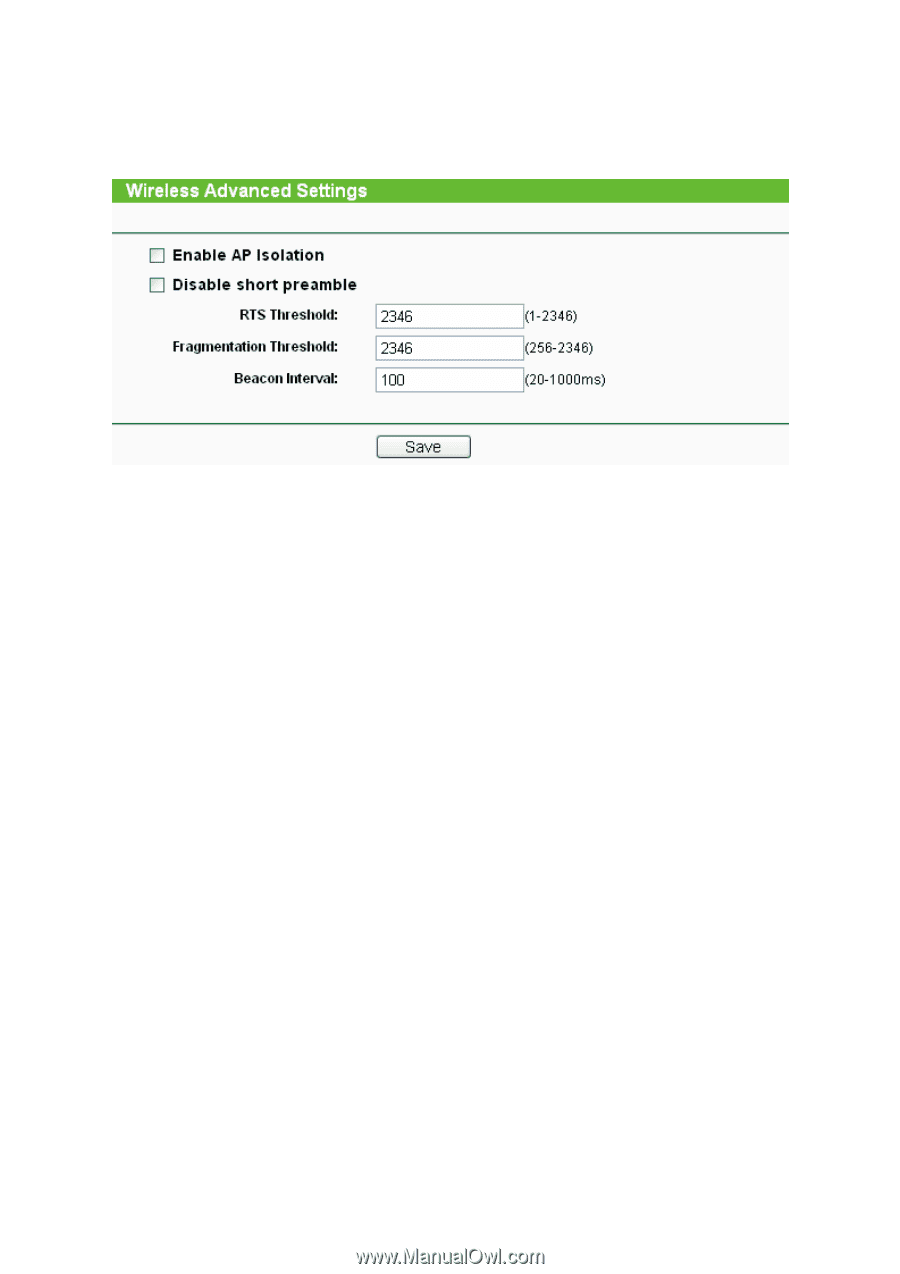
4.8 Wireless settings Selecting Wireless Settings will allow you to do some advanced settings for the device in the following screen as shown in Figure 4-26. Figure 4-26 Wireless settings ¾ Enable AP Isolation - Isolate all connected wireless stations so that wireless stations can not access each other through WLAN. This option is available only for AP mode. ¾ Disable short preamble - Disable short preamble and use long preamble only. It is recommended that you do not change these settings. ¾ RTS Threshold - RTS/CTS Threshold, the packet size that is used to determine if RTS/CTS should be sent. ¾ Fragmentation Threshold - The maximum packet size used for fragmentation. ¾ Beacon Interval - The interval time between two successive beacons. 4.9 Forwarding There are four submenus under the Forwarding menu (shown in Figure 4-27): Virtual Servers, Port Triggering, DMZ and UPnP. Click any of them, and you will be able to configure the corresponding function. The detailed explanations for each submenu are provided below. Virtual servers can be used for setting up public services on your LAN, such as DNS, Email and FTP. A virtual server is defined as a service port, and all requests from the Internet to this service port will be redirected to the computer specified by the server IP. Any PC that was used for a virtual server must have a static or reserved IP Address because its IP Address may change when using the DHCP function. Port Triggering is used for some applications that cannot work with a pure NAT router, like Internet games, video conferencing, Internet calling and so on, which require multiple connections. The DMZ host feature allows one local host to be exposed to the Internet for a special-purpose service such as Internet gaming or videoconferencing. DMZ host forwards all the ports at the same time. Any PC whose port is being forwarded must have its DHCP client function disabled and should have a new static IP Address assigned to it because its IP Address may change when using the DHCP function. The Universal Plug and Play (UPnP) feature allows the devices, such as Internet computers, to access the local host resources or devices as needed. UPnP devices can be automatically discovered by the UPnP service application on the LAN. 38