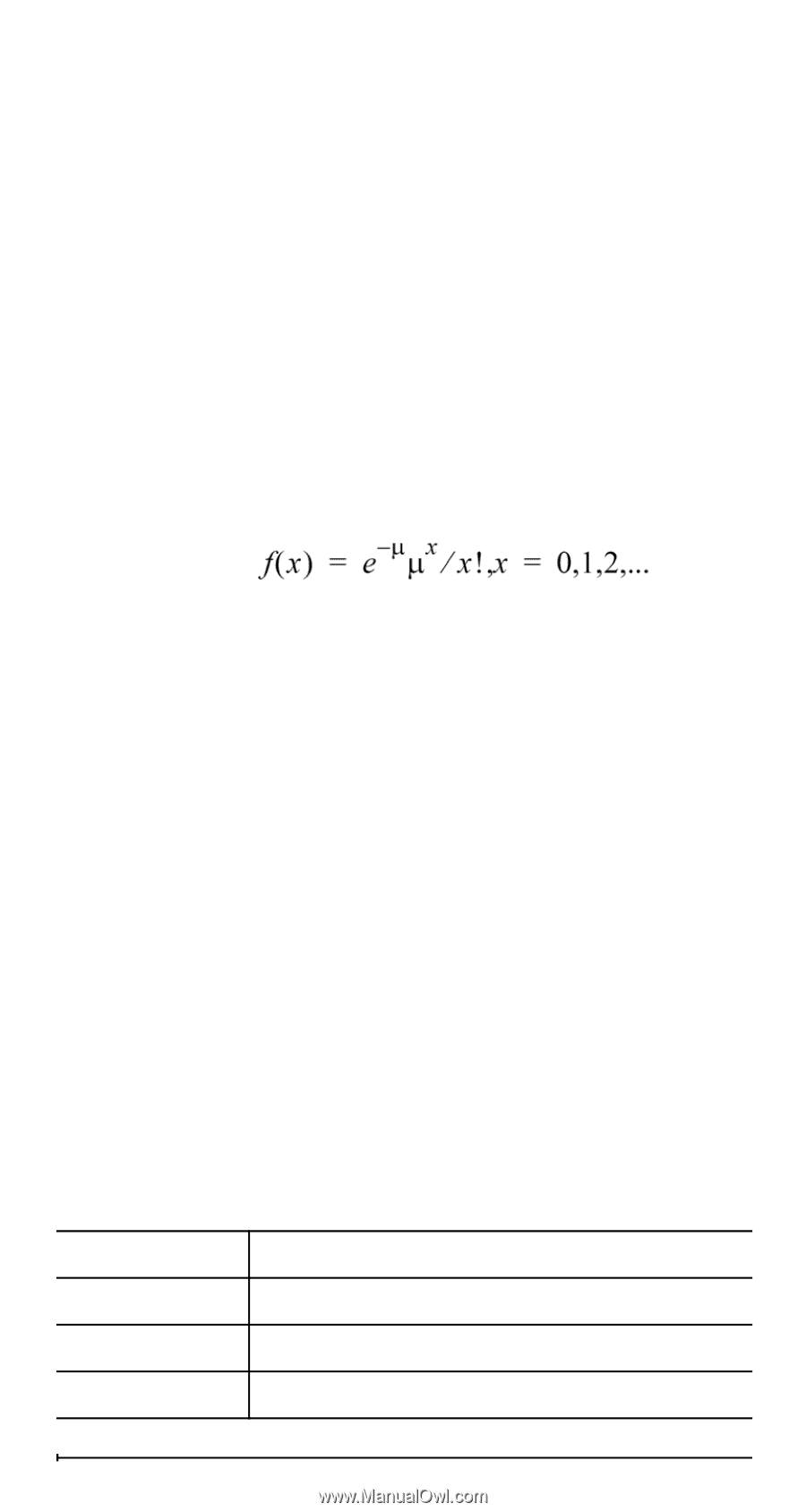Texas Instruments TI-36X Pro User Manual - Page 39
Poissonpdf, Poissoncdf, Important note about results, StatVars, Variables, Definition
 |
View all Texas Instruments TI-36X Pro manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 39 highlights
5: Binomcdf 6: Poissonpdf Computes a cumulative probability at x for the discrete binomial distribution with the specified numtrials and probability of success (p) on each trial. x can be nonnegative integer and can be entered with options of SINGLE, LIST or ALL (a list of cumulative probabilities is returned.) 0 { p { 1 must be true. Computes a probability at x for the discrete Poisson distribution with the specified mean mu (m), which must be a real number > 0. x can be an non-negative integer (SINGLE) or a list of integers (LIST). The probability density function (pdf) is: 7: Poissoncdf Computes a cumulative probability at x for the discrete Poisson distribution with the specified mean mu, which must be a real number > 0. x can be an non-negative integer (SINGLE) or a list of integers (LIST). Note: The default value for mu (m) is 0. For Poissonpdf and Poissoncdf, you must change it to a value > 0. 1-Var Stats and 2-Var Stats results Important note about results: Many of the regression equations share the same variables a, b, c, and d. If you perform any regression calculation, the regression calculation and the 2-Var statistics for that data are stored in the StatVars menu until the next statistics or regression calculation. The results must be interpreted based on which type of statistics or regression calculation was last performed. To help you interpret correctly, the title bar reminds you of which calculation was last performed. Variables n v or w Sx or Sy Definition Number of x or (x,y) data points. Mean of all x or y values. Sample standard deviation of x or y. 39