Texas Instruments TI-36X Pro User Manual - Page 55
Vector example - vectors
 |
View all Texas Instruments TI-36X Pro manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 55 highlights
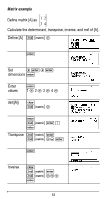
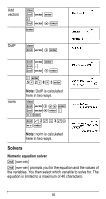
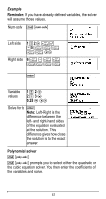
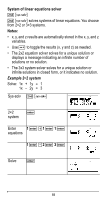
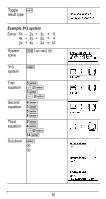
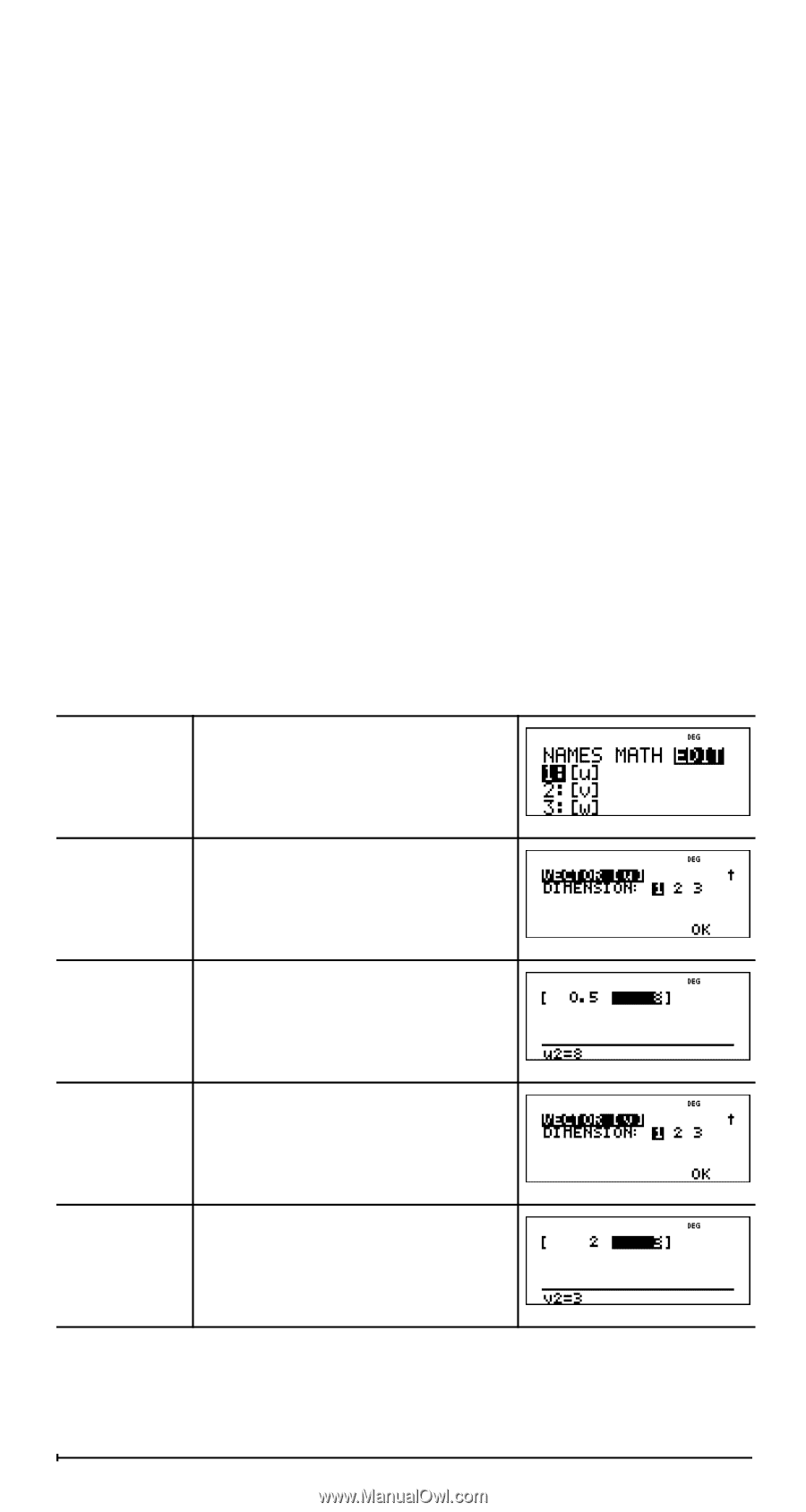
% ... MATH % ... " displays the vector MATH menu, which lets you perform the following vector calculations: 1: DotProduct 2: CrossProduct 3: norm magnitude Syntax: DotP(vector1, vector2) Both vectors must be the same dimension. Syntax: CrossP(vector1, vector2) Both vectors must be the same dimension. Syntax: norm(vector) % ... EDIT % ... ! displays the vector EDIT menu, which lets you define or edit vector [u], [v], or [w]. Vector example Define vector [u] = [ 0.5 8 ]. Define vector [v] = [ 2 3 ]. Calculate [u] + [v], DotP([u],[v]), and norm([v]). Define [u] % ... ! < " < < .5 < 8 < Define [v " < < 2 < 3 < 55
55
%
…
MATH
%
…
"
displays the vector
MATH
menu, which lets
you perform the following vector calculations:
%
…
EDIT
%
…
!
displays the vector
EDIT
menu, which lets you
define or edit vector [u], [v], or [w].
Vector example
Define vector [u] = [ 0.5
8 ]. Define vector [v] = [ 2
3 ].
Calculate [u] + [v],
DotP(
[u],[v]
)
, and
norm(
[v]
)
.
1: DotProduct
Syntax:
DotP(
vector1
,
vector2
)
Both vectors must be the same
dimension.
2: CrossProduct
Syntax:
CrossP(
vector1
,
vector2
)
Both vectors must be the same
dimension.
3: norm magnitude
Syntax:
norm(
vector
)
Define [u]
%
…
!
<
"
< <
.5
<
8
<
Define [v]
%
…
!
$
<
"
< <
2
<
3
<