Yamaha PSR-260 Owner's Manual - Page 52
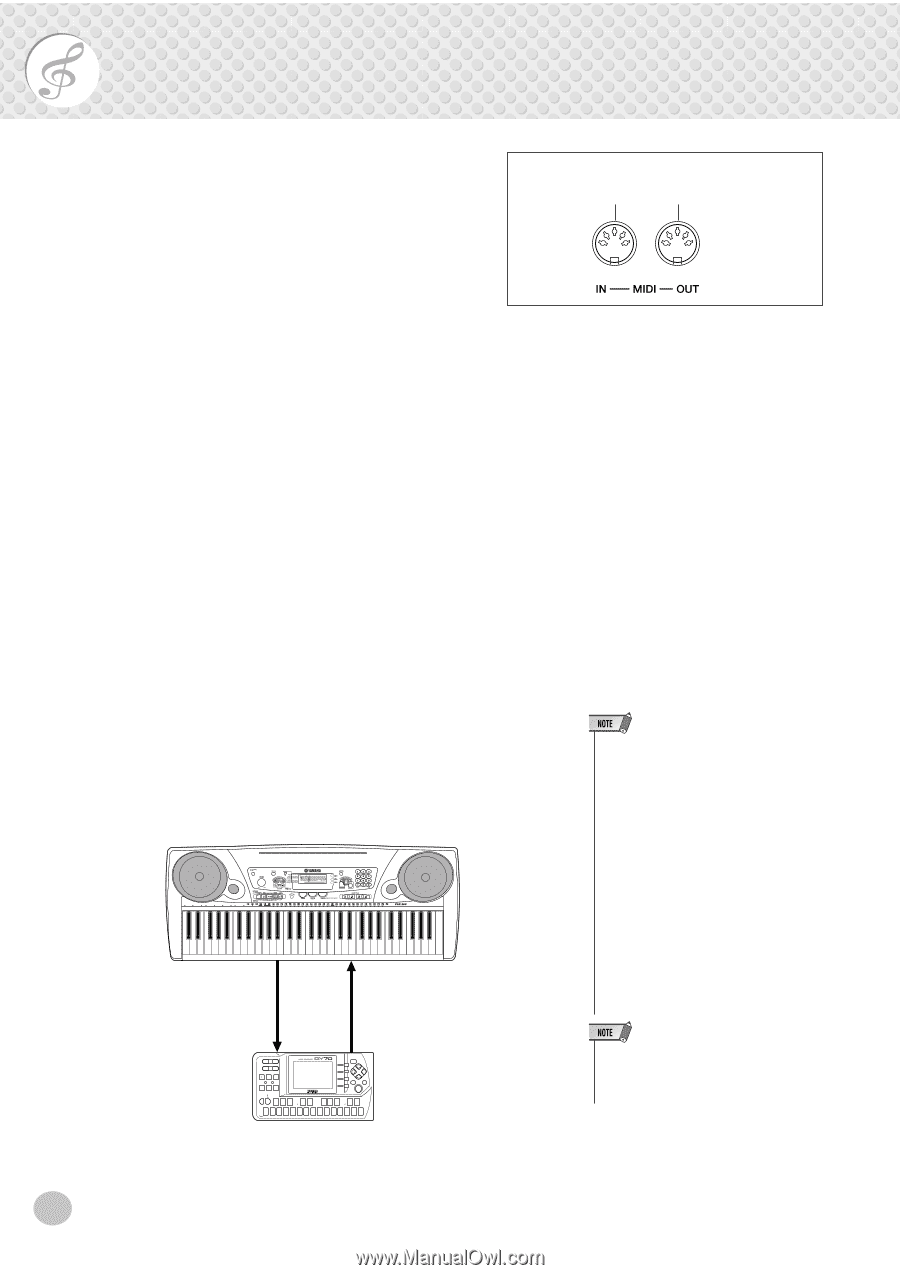
MIDI, into the proper MIDI channel. - midi cable
 |
View all Yamaha PSR-260 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 52 highlights
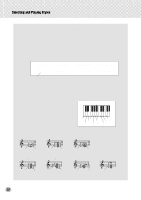
MIDI The PSR-260 also features MIDI terminals, allowing you to interface the PSR-260 with other MIDI instruments and devices. Receives MIDI data from the connected sending device. Transmits MIDI data (keyboard performance) to the connected device. s About MIDI MIDI (Musical Instrument Digital Interface) is a worldwide standard that is built into many electronic musical instruments and other digital music related devices, allowing them to be connected and "communicate" with each other. For two MIDI instruments to communicate, they must be connected by MIDI cables. In a basic example, the MIDI IN and MIDI OUT terminals of the PSR-260 could be connected to the MIDI OUT and MIDI IN terminals of a sequencer, allowing you to record and play back performance data from the PSR-260. The instruments communicate with each other by sending "messages" or MIDI data. The sending instrument usually assigns the data to one of sixteen MIDI channels, then transmits it over the MIDI cable. The cable itself, however, is not divided up into sixteen channels. Just as with a television set that receives programs on different channels, it is up to the receiving instrument to "tune into" the proper MIDI channel. If the sending and receiving channels on the respective instruments do not match, the receiving instrument may not understand or respond to the one sending. s How Can MIDI be Used In the simple, yet powerful MIDI application example below, the Yamaha QY-70 Music Sequencer is used to record and play back performance data played on the PSR-260 keyboard. Before actually recording to the sequencer, press the [ACCOMPANIMENT ON/OFF] button once or twice to make sure that the current settings are sent. 001 GrandPno TEMPO 116 Connect the MIDI OUT of the PSR-260 to the MIDI IN of the QY-70 Connect the MIDI IN of the PSR-260 to the MIDI OUT of the QY-70 • On the PSR-260, the following channels (eight total) are enabled for MIDI reception: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 10. The MIDI transmit channels are fixed to the following data: Ch. 1 : Keyboard, harmony Ch. 2 : Bass Ch. 3 : Chord Ch. 4 - 7 : Other Ch. 10 : Rhythm • Parts that have been recorded using the PSR-260 should also be played back from the PSR-260. Data may not play back as expected when using other sound sources (such as the internal sounds of the QY-70). Also, a connected sound source may sound at a different octave from that originally played on the PSR-260. • MIDI data cannot be transmitted during song playback. • Avoid using MIDI cables 15 meters or longer, since doing so can result in MIDI errors. Viewing the Notation for MIDI Channel 1 • The PSR-260 has a special function that lets you view the notes of the MIDI data (channel 1 only) on the display. 52