Yamaha PSR-350 Owner's Manual - Page 48
The Intervals of the Scale, Other Chords, chord includes the 6th note of the scale
 |
View all Yamaha PSR-350 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 48 highlights
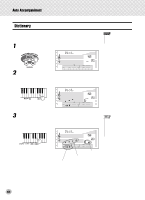
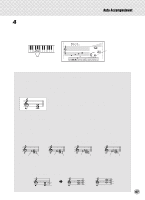
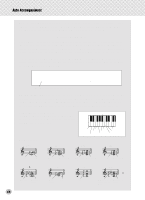
Auto Accompaniment Beautiful sounding harmonies can be built in this manner. The use of intervals and chords is one of the most important elements in music. A wide variety of emotions and feelings can be created depending on the types of chords used and the order in which they are arranged. Writing Chord Names Knowing how to read and write chord names is an easy yet invaluable skill. Chords are often written in a kind of shorthand that makes them instantly recognizable (and gives you the freedom to play them with the voicing or inversion that you prefer). Once you understand the basic principles of harmony and chords, it's very simple to use this shorthand to write out the chords of a song. First, write the root note of the chord in an uppercase letter. If you need to specify sharp or flat, indicate that to the right of the root. The chord type should be indicated to the right as well. Examples for the key of C are shown below. Major chord C Minor chord Cm Augmented chord Caug Diminished chord Cdim For simple major chords, the type is omitted. One important point: Chords are made up of notes "stacked" on top of each other, and the stacked notes are indicated in the chord name of the chord type as a number - the number being the distance of the note from the root. (See the keyboard diagram below.) For example, the minor 6th chord includes the 6th note of the scale, the major 7th chord has the 7th note of the scale, etc. The Intervals of the Scale To better understand the intervals and the numbers used to represent them in the chord name, study this diagram of the C major scale: Other Chords Dominant 7th (flatted 7th) CDEFGABCDE F Root 4th 7th 3rd 6th 2nd 5th 11th 9th Octave Csus4 C7 Cm7 CM7 5th 4th Cm7b5 Dominant Diminished 7th chord Dominant Major chord 7th Cm6 Minor 6th chord Dominant Minor chord 7th 7th Major chord C(9) 9th Cdim7 * Bbb = A Diminished 7th Diminished (double flatted chord 7th) 48