Yamaha PSR-630 Owner's Manual - Page 121
MIDI Functions, What’s MIDI
 |
View all Yamaha PSR-630 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 121 highlights
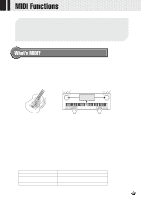
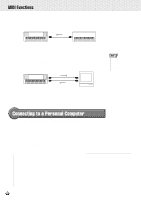
,,QQ,,QQM,,QQID,,QQI Fu,,QQnct,,QQion,,QQs ,,QQ,,QQ,,QQ,,QQ,,QQ,,QQ,,QQ,,QQ,,QQ In the rear panel of your PSR-730/630, there are MIDI terminals (MIDI IN, MIDI OUT), a TO HOST terminal, and a HOST SELECT switch. By using the MIDI functions you can expand your musical possibilities. This section explains what MIDI is, and what it can do, as well as how you can use MIDI on your PSR-730/630. What's MIDI? No doubt you have heard the terms "acoustic instrument" and "digital instrument." In the world today, these are the two main categories of instruments. Let's consider an acoustic piano and a classical guitar as representative acoustic instruments. They are easy to understand. With the piano, you strike a key, and a hammer inside hits some strings and plays a note. With the guitar, you directly pluck a string and the note sounds. But how does a digital instrument go about playing a note? q Acoustic guitar note production q Digital instrument note production L Tone Generator Sampling (Electronic circuit) Sampling R Note Note Playing the keyboard Pluck a string and the body resonates the sound. Based on playing information from the keyboard, a sampling note stored in the tone generator is played through the speakers. As shown in the illustration above, in an electronic instrument the sampling note (previously recorded note) stored in the tone generator section (electronic circuit) is played based on information received from the keyboard. So then what is the information from the keyboard that becomes the basis for note production? For example, let's say you play a "C" quarter note using the grand piano sound on the PSR-730/630 keyboard. Unlike an acoustic instrument that puts out a resonated note, the electronic instrument puts out information from the keyboard such as "with what voice," "with which key," "about how strong," "when was it pressed," and "when was it released." Then each piece of information is changed into a number value and sent to the tone generator. Using these numbers as a basis, the tone generator plays the stored sampling note. Example of Keyboard Information Voice number (with what voice) Note number (with which key) Note on (when was it pressed) and note off (when was it released) Velocity (about how strong) 01 (grand piano) 60 (C3) Timing expressed numerically (quarter note) 120 (strong) 119