Yamaha PSR-630 Owner's Manual - Page 122
Data Format and MIDI Implementation Chart on s 168 and 169., System Messages, Channel Messages
 |
View all Yamaha PSR-630 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 122 highlights
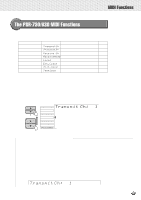
,,QQ,,QQMID,,QQI Func,,QQtions,,QQ,,QQ,,QQ,,QQ,,QQ,,QQ,,QQ,,QQ,,QQ,,QQ,,QQ,,QQ MIDI is an acronym that stands for Musical Instrument Digital Interface, which allows electronic musical instruments to communicate with each other, by sending and receiving compatible Note, Control Change, Program Change and various other types of MIDI data, or messages. The PSR-730/630 can control a MIDI device by transmitting note related data and various types of controller data. The PSR-730/630 can be controlled by the incoming MIDI messages which automatically determine tone generator mode, select MIDI channels, voices and effects, change parameter values and of course play the voices specified for the various parts. MIDI messages can be divided into two groups: Channel messages and System messages. Below is an explanation of the various types of MIDI messages which the PSR-730/630 can receive/transmit. q Channel Messages The PSR-730/630 is an electronic instrument that can handle 16 channels. This is usually expressed as "it can play 16 instruments at the same time." Channel messages transmit information such as Note ON/OFF, Program Change, for each of the 16 channels. Message Name Note ON/OFF Program Change Control Change PSR-730/630 Operation/Panel Setting Messages which are generated when the keyboard is played. Each message includes a specific note number which corresponds to the key which is pressed, plus a velocity value based on how hard the key is stuck. Voice setting (control change bank select MSB/LSB setting) Revoice setting(volume, pan pot, etc.) q System Messages This is data that is used in common by the entire MIDI system. System messages include messages like Exclusive Messages that transmit data unique to each instrument manufacturer and Realtime Messages that control the MIDI device. Message Name Exclusive Message Realtime Messages PSR-730/630 Operation/Panel Setting Reverb/chorus/DSP settings, etc. Clock setting Start/stop operation The messages transmitted/received by the PSR-730/630 are shown in the MIDI Data Format and MIDI Implementation Chart on pages 168 and 169. 120