HP ProLiant DL320e HP Power Regulator for ProLiant servers
HP ProLiant DL320e Manual
 |
View all HP ProLiant DL320e manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
HP ProLiant DL320e manual content summary:
- HP ProLiant DL320e | HP Power Regulator for ProLiant servers - Page 1
for ProLiant servers technology brief, 4th edition Abstract...2 Introduction...2 Processor P-states...2 Power Regulator technology...3 Power Regulator modes ...3 HP Static High Performance mode...4 HP Static Low Power mode...4 HP Dynamic Power Savings mode...4 Configuring Ultra Low Power state - HP ProLiant DL320e | HP Power Regulator for ProLiant servers - Page 2
fact, delay the expansion of existing server systems. HP Power Regulator is a standard feature on HP ProLiant servers 200-series and above. It leverages processor power state registers exposed by processor vendors. Power Regulator enables control of processor power usage and performance to minimize - HP ProLiant DL320e | HP Power Regulator for ProLiant servers - Page 3
in the system firmware, providing a consistent mechanism for optimizing processor power use in all servers, regardless of the operating system in use. Figure 1. Methods for controlling processor P-states OS Control Mode OS Driver System ROM Hardware Registers HP Power Regulator Dynamic and - HP ProLiant DL320e | HP Power Regulator for ProLiant servers - Page 4
ProLiant servers and processor models. Beginning with G5 servers, however, all Power Regulator modes are supported on all ProLiant 200series and above server models. For a detailed list of processors supported by Power Regulator, consult the Power Regulator website at http://www.hp.com/servers/power - HP ProLiant DL320e | HP Power Regulator for ProLiant servers - Page 5
does not support dynamic power management, or if the feature has not been configured through the operating system, the processor will always run in its highest power and performance state. NOTE: Some earlier ProLiant servers refer to this option as Power Regulator Disabled. Power Regulator and - HP ProLiant DL320e | HP Power Regulator for ProLiant servers - Page 6
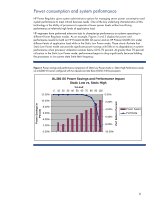
both an HP ProLiant DL380 G5 server and an HP ProLiant DL385 G5 under different levels of application load while in the Static Low Power mode. These charts illustrate that Static Low Power mode can provide significant power savings with little or no degradation in system performance when processor - HP ProLiant DL320e | HP Power Regulator for ProLiant servers - Page 7
and performance comparison of Static Low Power mode vs. Static High Performance mode on a DL385 G5 server configured with two AMD 2356 2.3 GHz processors Power Savings in Percent Perf Delta (Iterations/s) DL385 G5 Power Savings and Performance Impact Ultra Static Low vs. Static High % Load - HP ProLiant DL320e | HP Power Regulator for ProLiant servers - Page 8
Pwr Saved Perf Delta Figure 5. Power savings and performance comparison of Dynamic Power Savings mode vs. Static High Performance mode on a DL385 G5 server configured with two Quad-core AMD Opteron 2356 2.3 GHz processors Power Savings (Watts) DL385 G5 Power Savings and Performance Impact Dynamic - HP ProLiant DL320e | HP Power Regulator for ProLiant servers - Page 9
secondary effects on memory power consumption as well as on the efficiencies of power supplies and voltage regulators. Thus the total power saved in a particular system is dependent on the number of processors, DIMMs, I/O cards, and drives installed, as well as the processor utilization. The maximum - HP ProLiant DL320e | HP Power Regulator for ProLiant servers - Page 10
mode on a DL385 G5 server Percent Gain in Performance per Watt ProLiant DL385 G5 Static Low vs. Static High Dynamic vs. Static High 25.0 20.0 15.0 10.0 5.0 0.0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 Processor Utilization (%) Power management and reporting HP Insight Power Manager (IPM) and Integrated - HP ProLiant DL320e | HP Power Regulator for ProLiant servers - Page 11
Regulator mode for one to many ProLiant servers. System Administrators can make Power Regulator changes interactively through the web user interface or schedule the changes to occur at specific and recurring times. For additional information and supported servers go to http://www.hp.com/go/ipm 11 - HP ProLiant DL320e | HP Power Regulator for ProLiant servers - Page 12
Lights-Out (iLO) and Integrated Lights-Out 2 (iLO 2) Both the iLO and iLO2 management processors can be used to control Power Regulator. The iLO reporting and management tools are limited to individual server management. Management Power Regulator can be managed using the iLO user interface - HP ProLiant DL320e | HP Power Regulator for ProLiant servers - Page 13
as database, Exchange, file and print, web server, and OLTP. Consider the effect of Power Regulator on an HP ProLiant DL385 G5 server running a database with an average processor load of 50 percent. The application involved a mixture of cache, memory, arithmetic, and floating point activities. The - HP ProLiant DL320e | HP Power Regulator for ProLiant servers - Page 14
a DL385 G5 server at various system loads Power (Watts) DL385 G5 Power Consumption vs. Load 350 325 300 275 250 225 200 175 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 Processor Utilization (%) Static High Dynamic Static Low Table 3. Calculated annual power cost savings for an HP ProLiant DL385 G5 server - HP ProLiant DL320e | HP Power Regulator for ProLiant servers - Page 15
in cluster environments. Figure 10 indicates the difference in system power consumption for Static High Performance, Dynamic Power Savings, and Static Low Power modes of Power Regulator over varying loads. The same server configuration used in the previous test was used to gather this data - HP ProLiant DL320e | HP Power Regulator for ProLiant servers - Page 16
Regulator allows IT administrators to directly reduce the frequency and core voltage of the processors. This, in turn, can significantly reduce costs for power and cooling. Administrators can monitor power consumption, keeping track of its use in relation to data center limitations. This capability - HP ProLiant DL320e | HP Power Regulator for ProLiant servers - Page 17
at http://www.hp.com/servers/powerregulator. Call to action Send comments about this paper to [email protected]. © 2007, 2008 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P. The information contained herein is subject to change without notice. The only warranties for HP products and services are set forth

Power Regulator for ProLiant servers
technology brief, 4th edition
Abstract
..............................................................................................................................................
2
Introduction
.........................................................................................................................................
2
Processor P-states
.................................................................................................................................
2
Power Regulator technology
..................................................................................................................
3
Power Regulator modes
....................................................................................................................
3
HP Static High Performance mode
......................................................................................................
4
HP Static Low Power mode
................................................................................................................
4
HP Dynamic Power Savings mode
......................................................................................................
4
Configuring Ultra Low Power state
.....................................................................................................
4
OS Control mode
.............................................................................................................................
4
Power Regulator and Dynamic Power Savings
.........................................................................................
5
Measuring CPU utilization
.................................................................................................................
5
Processor granularity
........................................................................................................................
5
Power consumption and system performance
..........................................................................................
6
Power management and reporting
.......................................................................................................
10
Insight Power Manager
...................................................................................................................
10
Integrated Lights-Out (iLO) and Integrated Lights-Out 2 (iLO 2)
.............................................................
12
Management
.............................................................................................................................
12
Reporting
..................................................................................................................................
12
Typical uses for Power Regulator
.........................................................................................................
13
Reducing power and cooling cost
....................................................................................................
13
Increasing server density and performance per watt
...........................................................................
15
Ensuring uptime
.............................................................................................................................
15
Summary
..........................................................................................................................................
16
For more information
..........................................................................................................................
17
Call to action
....................................................................................................................................
17